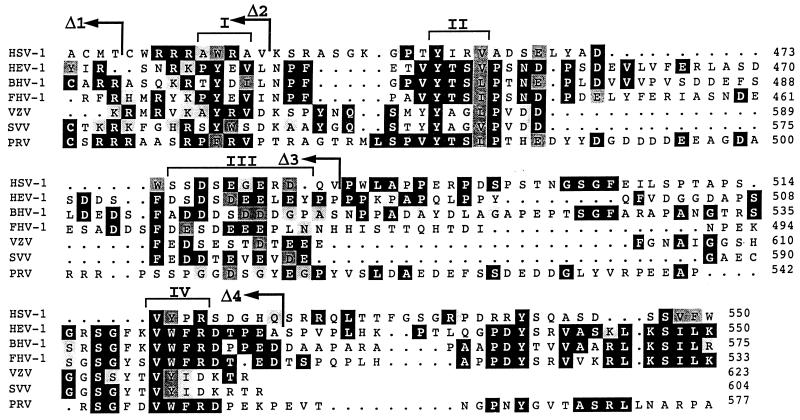
FIG. 5.
Multiple sequence alignment of the cytoplasmic tails of the gE homologs forms seven different members of the Alphaherpesvirinae subfamily. The sequences shown include those of HSV-1 (47), HEV-1 (72), BHV-1 (36), FHV-1 (48), VZV (15), SVV (21), and PRV (56). The sequences of the gE homologs from HSV-1, HEV-1, BHV-1, VZV, SVV, and PRV are under SwissProt accession no. vgle_hsv11, vgle_hsveb, vgle_hsvbs, vgle_vzvd, vgle_svvd, and vgl_prvri, respectively, and FHV-1 gE is under GenBank accession no. X98449. Identical amino acids found in at least three of the seven sequences are shown as white characters on a black background, and conserved substitutions are shown on a grey background. Brackets on top of the alignment indicate the conserved regions discussed in the text. The amino acid positions for every sequence (considering the full-length precursor proteins) at the end of each block in the alignment are shown in the right-hand margin. The last amino acids of the different HSV-gE truncation mutants (Δ1, Δ2, Δ3, and Δ4) are indicated by arrows.