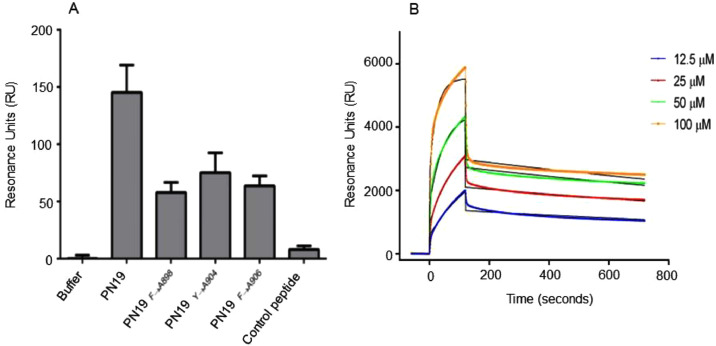
Fig. 7.
MPER25c SPR binding activity of PN19 peptide and its derivatives. A- Binding levels to immobilized MPER25c peptide of peptide PN19 compared to PN19F→A898, PN19Y→A904, PN19F→A906 at the concentration 100 µM. peptide MPER25c was covalently immobilized onto the gold surface of the biosensor following the thiol coupling immobilization strategy. All peptides were flowed separately over the immobilized MPER25c fragment in individual cycle of analysis with an initial association phase (sample injection), a second dissociation phase (washing step with running buffer), and finally a chip surface regeneration phase. Background levels due to non-specific peptide interactions were monitored on the reference channel of the chip and subtracted from sample signals. The running buffer and a control peptide has been also tested as negative controls. B- Sensorgrams of interaction between peptide PN19 and the immobilized MPER25c at different concentrations comprising the theoretical curves for a 1:1 binding model (black).