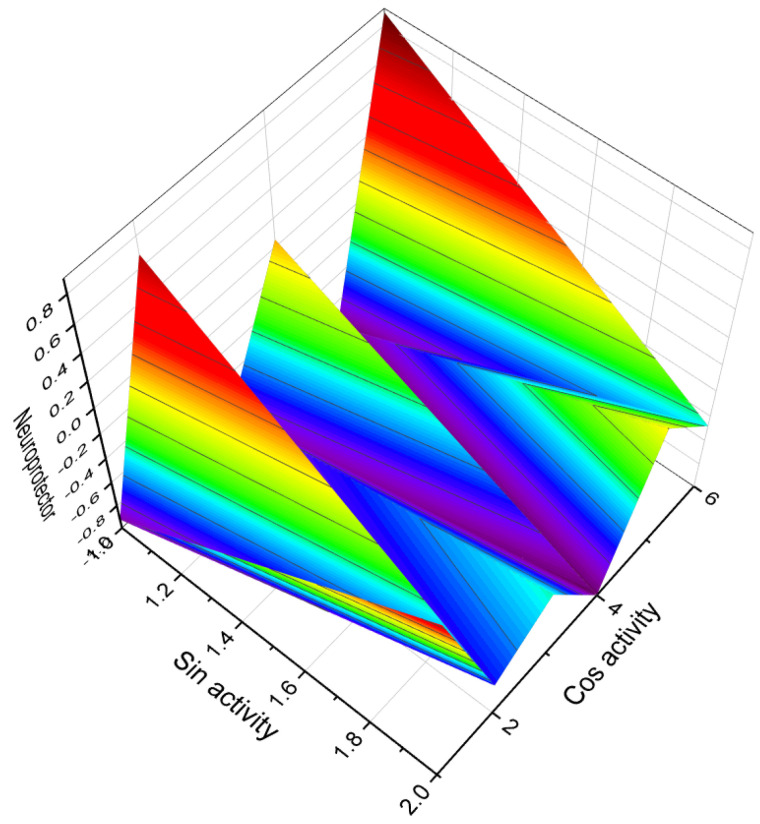
Figure 8.
A 3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated activity of the compound 4-hydroxy-6-oxopregnane-3-glycoside (29) as a neuroprotector. The graph demonstrates the relationship between the compound’s structure and its predicted neuroprotective activity with a confidence level exceeding 97%. This steroid, containing an aromatic ring A, was isolated from a Pohnpei sponge known as Cribrochalina olemda. The graph provides insight into the relationship between the molecular structure of the compound and its predicted efficacy as a neuroprotector. By analyzing the graph, one can observe how variations in the structural features of the compound may impact its potential neuroprotective effects. The high confidence level of over 97% suggests a strong reliability in the predicted activity of this steroid as a neuroprotector. Understanding the neuroprotective activity of compounds is crucial for the development of potential treatments or interventions for neurodegenerative disorders, brain injuries, and other conditions that affect the health and function of the nervous system. Neuroprotector activity refers to the ability of a compound to protect and preserve the health and function of neurons in the brain and nervous system.