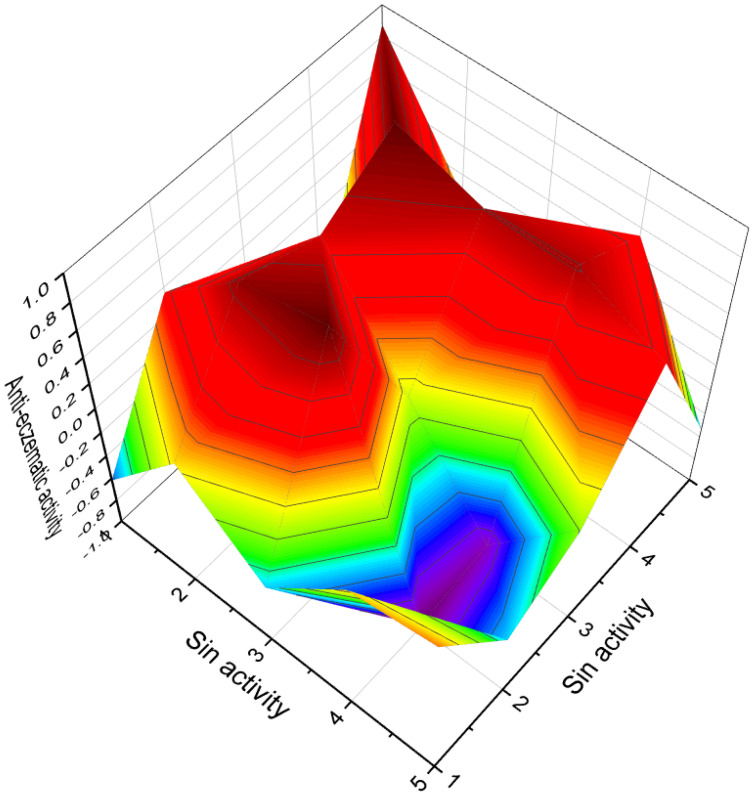
Figure 27.
A 3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated anti-eczematic activity of chlorinated steroids, specifically compounds 115, 116, 117, 124, and 132. The graph provides insights into the relationship between the activity of these compounds and their potential efficacy in treating eczema. Anti-eczematic activity refers to the ability of a compound to alleviate or manage symptoms associated with eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by itching, redness, and rash. Compounds with anti-eczematic activity can help reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and promote skin healing. The predicted and calculated activity values depicted on the graph represent the potency or effectiveness of the chlorinated steroids in terms of their anti-eczematic properties. With a confidence level of over 91%, the graph indicates a high degree of certainty in the accuracy of the predicted and calculated activity values. The exploration of chlorinated steroids for their anti-eczematic activity holds promise in the field of dermatology and skin health. Identifying compounds that can effectively reduce inflammation, alleviate itching, and promote skin repair can significantly improve the management of eczema. It is important to note that further research, including in vitro and clinical studies, is necessary to fully understand the mechanisms of action, optimal dosage, and potential applications of these chlorinated steroids in treating eczema. Additionally, comprehensive safety evaluations would be required to assess their suitability for use in human subjects.