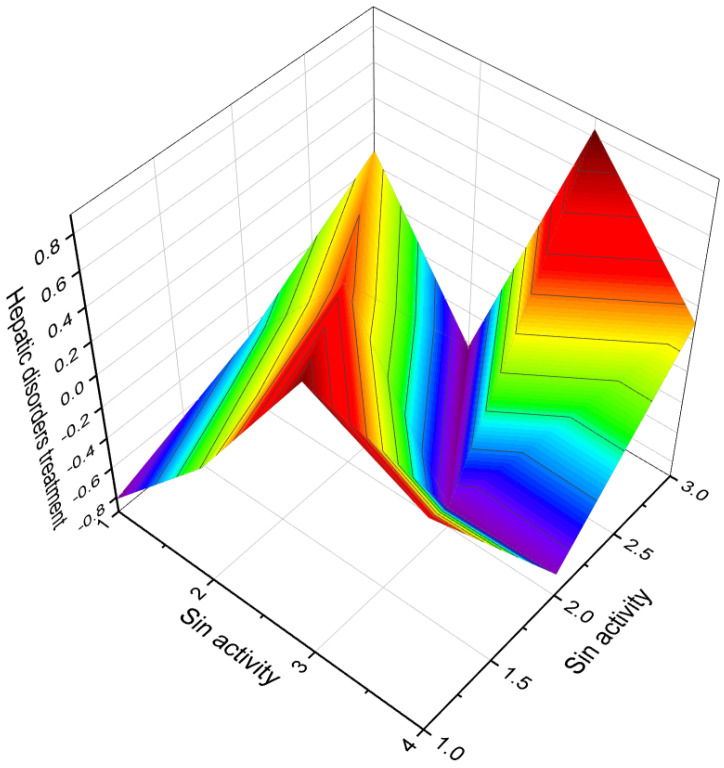
Figure 30.
A 3D graph depicting the predicted and calculated activity of chlorinated steroids, specifically compounds 141, 142, and 143, as potential treatments for liver disease. The graph provides insights into the relationship between the activity of these compounds and their potential efficacy in treating liver diseases. Liver disease refers to a wide range of conditions that affect the liver, impairing its normal functioning. These conditions can include liver inflammation (hepatitis), fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and others. Treatment options for liver disease are diverse, including medications that can help manage symptoms, slow down disease progression, or promote liver regeneration. The predicted and calculated activity values displayed on the graph represent the potency or effectiveness of the chlorinated steroids in terms of their activity against liver disease. With a confidence level of over 93%, the graph indicates a high degree of certainty in the accuracy of the predicted and calculated activity values. The exploration of chlorinated steroids for their potential therapeutic effects in liver disease is an area of active research. These compounds may interact with various molecular targets and pathways involved in liver function, inflammation, and regeneration, potentially offering benefits in the management of liver diseases.