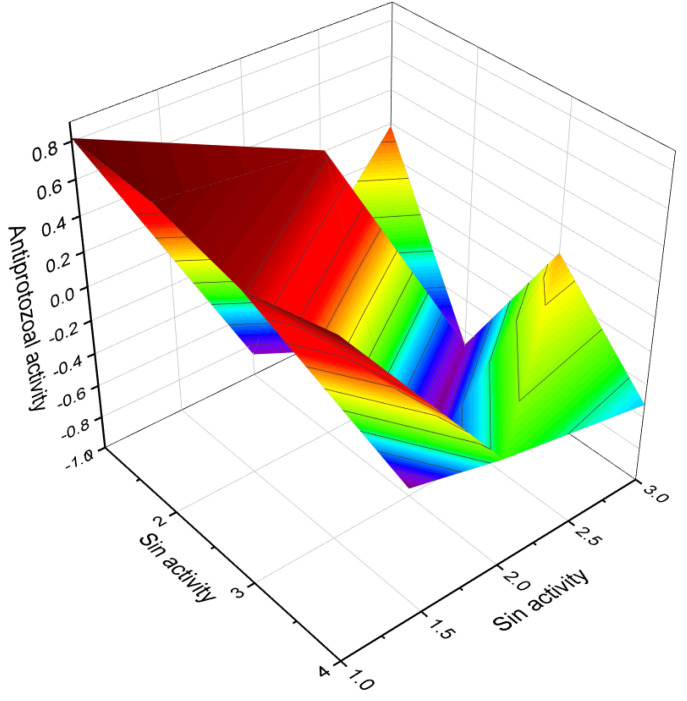
Figure 31.
A 3D graph illustrating the predicted and calculated anti-protozoal activity of chlorinated steroids, specifically compounds 148, 149, and 150. The graph provides insights into the relationship between the activity of these compounds and their potential efficacy in inhibiting protozoan parasites. Anti-protozoal activity refers to the ability of a compound to inhibit the growth or survival of protozoan parasites, which are single-celled organisms that can cause various infectious diseases in humans and animals. Protozoan parasites can cause diseases such as malaria, leishmaniasis, trypanosomiasis, and toxoplasmosis, among others. The predicted and calculated activity values depicted on the graph represent the potency or effectiveness of the chlorinated steroids in terms of their anti-protozoal properties. With a confidence level of over 95%, the graph indicates a high degree of certainty in the accuracy of the predicted and calculated activity values. The exploration of chlorinated steroids for their anti-protozoal activity is of great interest in the field of parasitology and drug discovery. Identifying compounds that can effectively target and inhibit protozoan parasites can lead to the development of new treatments for various protozoal infections.