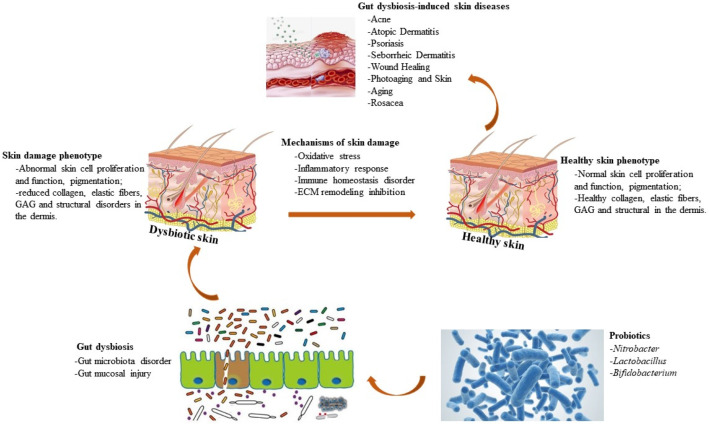
Figure 5.
The mechanism of probiotics to improve skin diseases. Probiotics, including Nitrobacter, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, can restore intestinal homeostasis by improving intestinal microbiota disorders and repairing intestinal mucosal damage, and then treat skin damage phenotype, including abnormal skin cell proliferation and function, pigmentation, reduced collagen, elastic fibers, glycosaminoglycan (GAG), and structural disorders in the dermis by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation response, immune homeostasis, and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling inhibition, ultimately treating skin diseases (acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, wound healing, photoaging and aging skin, and rosacea).