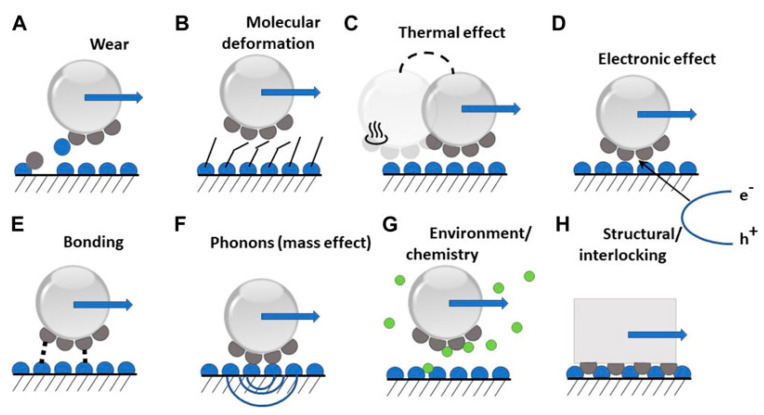
Figure 2.
Schematic representations of various mechanisms associated with energy dissipation during sliding, including: (A) wear, (B) molecular deformation, (C) thermal effect, (D) electronic effect, (E) bonding, (F) phonons, (G) environment/chemistry, and (H) structural/interlocking [20]. Copyright © 2023 American Chemical Society.