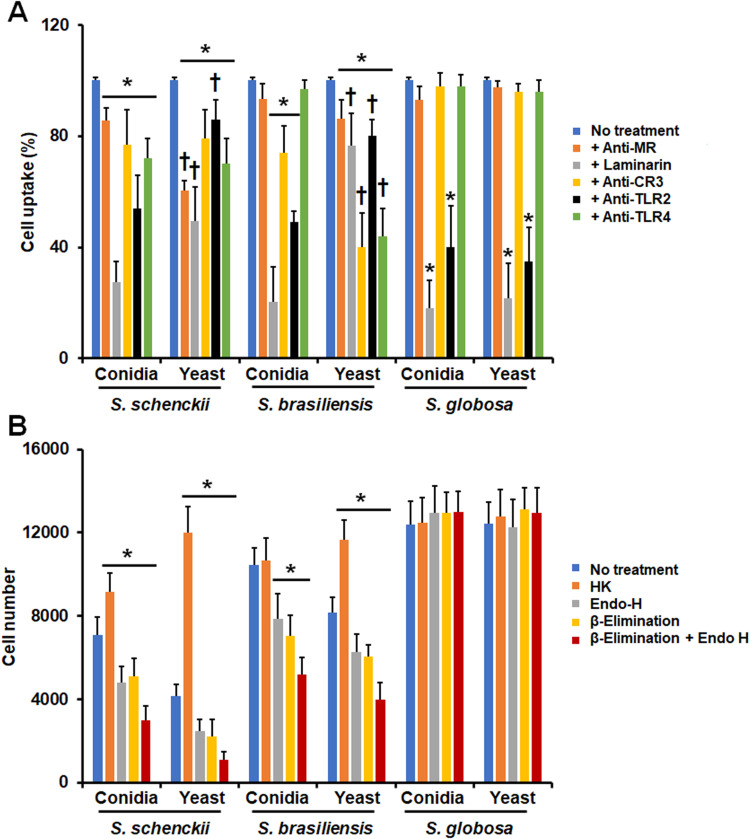
Figure 2.
Contribution of pattern recognition receptors and cell wall components on the phagocytosis of Sporothrix schenckii, Sporothrix brasiliensis, and Sporothrix globosa by human monocyte-derived macrophages. In (A), Human monocyte-derived macrophages were preincubated with 200 μg mL−1 laminarin or 10 μg mL−1 of any of the following antibodies: anti-mannose receptor (MR), anti-CR3, anti-TLR2, or anti-TLR4. Then, cells were coincubated with Acridine Orange-labeled conidia or yeast-like cells at a macrophage-fungus ratio of 1:6, for 2 h at 37°C and 5% (v/v) CO2. Human cells were analyzed by flow cytometry, collecting 50,000 events, which were defined as a human cell interacting with at least one fungal cell. All the interactions were performed in the presence of 5 μg mL−1 polymyxin B. No treatment, cells preincubated with PBS. Results correspond to cells in the late stage of phagocytosis. For all cases, 100% corresponds to human cells preincubated with PBS, and the absolute values were similar to those shown in Figure 1 or (B) of this figure. CR3, complement receptor 3. *P < 0.05 when compared to the no-treatment condition of the same strain. †P< 0.05 when compared to conidia from the same species. In (B), Similar experiments as described in (A), but human cells were not preincubated with any blocking agent. Before coincubation with human monocyte-derived macrophages, conidia, and yeast-like cells were inactivated by heat (HK), treated with endoglycosidase H (Endo-H), β-eliminated to remove O-linked glycans, or both treated with endoglycosidase H and β-elimination. No treatment refers to live cells without any treatment. *P < 0.05 when compared to the no-treatment condition of the same strain. For both panels, data were shown as means ± SD from eight donors analyzed by duplicate.