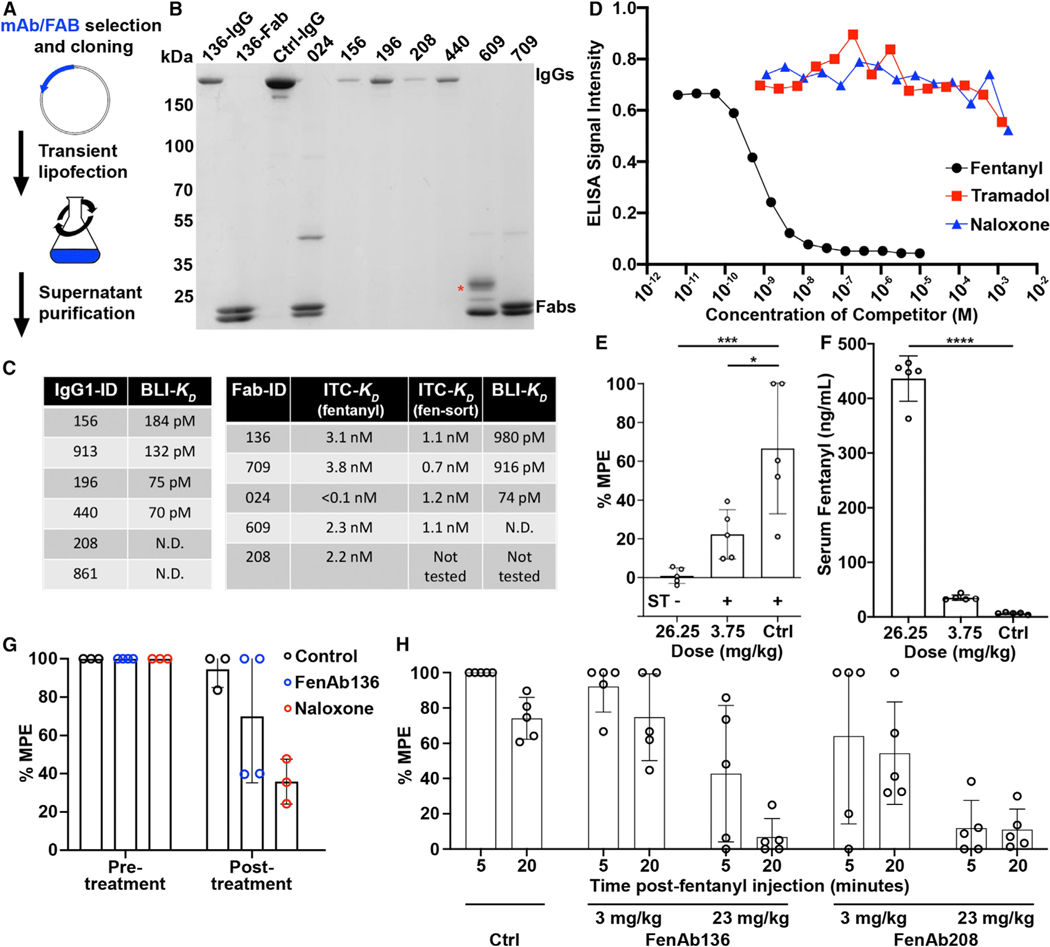
Figure 5. Fentanyl-specific antibodies are of high affinity and specificity and protect mice from fentanyl pharmacological effects.
(A) Schematic of the expression system used to produce recombinant antibodies.
(B) Coomassie-stained non-reducing SDS-PAGE after affinity purification of a panel of the expressed IgGs (running near 150 kDa) and Fabs (running as separate heavy and light chains near 25 kDa). The red asterisk marks a band produced by a glycosylated Fab, while the remaining Fabs are not glycosylated. The first lane marked “136” is the full-length IgG version of this antibody, while the second lane is the Fab. 156, 196, 208, and 440 are IgG protein samples, while 024, 609, and 709 are Fab protein samples. Ctrl-IgG is a control IgG sample as an additional molecular weight reference.
(C) Binding affinities determined for each antibody using both ITC and BLI. Antibodies whose affinity were too high to measure are here reported as “not determinable” (N.D.).
(D) Competition ELISA data generated with haptenated fentanyl-coated plates. The indicated soluble competitors are serially diluted into the assay to determine the relative efficiency of cross-binding to other opioid molecules, with soluble fentanyl serving as a positive control.
(E) Behavioral protection from fentanyl after prophylactic passive immunization with FenAb136. A positive (+) or negative (−) reaction in the ST test is indicated below and representative of the whole group. Means ± SD of 5 mice per group are shown. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.005 by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.
(F) Sera from the mice in (E) were collected and analyzed for fentanyl content by mass spectrometry. Means ± SD of 5 mice per group are shown. ****p < 0.001 by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.
(G) Behavioral protection from fentanyl after therapeutic (rescue) passive immunization with FenAb136. Hot plate assay recordings were made at T = 15 and 30 min post-fentanyl injection. Means ± SD of >3 mice per group are shown.
(H) Behavioral protection from fentanyl after prophylactic passive immunization with FenAb136 or FenAb208. Means ± SD of 5 mice per group are shown.
See also Figure S5.