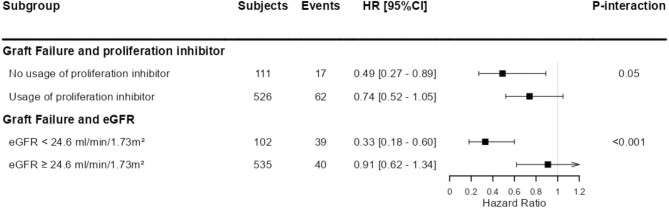
Figure 1:
Stratified analysis of the association of urinary lithium excretion with risk of graft failure, according to effect modifiers. P for interaction <.05 was considered to indicate a significant effect modification. Stratified Cox proportional hazards regression analyses were performed to assess the association of log2 transformed urinary lithium excretion with the risk of graft failure and kidney function decline according to significant effect modifiers. The used cut-offs for eGFR for stratified analyses were chosen to obtain a comparable number of events per group. Coefficient estimates are shown with adjustment for age, sex, BSA, eGFR and urinary protein excretion. The arrow indicates the upper limit of the CI is larger than the figure limit of 1.2.