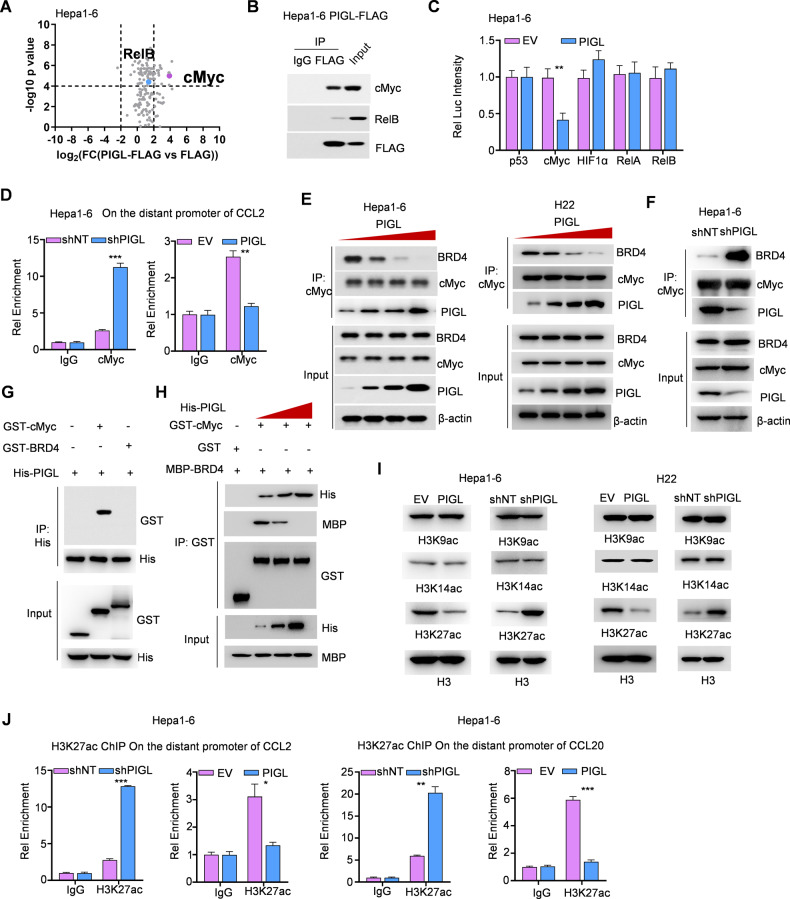
Fig. 5.
PIGL targeted cMyc to disrupt the cMyc/BRD4 axis and then reduced H3K27ac levels on the distant CCL2/20 promoter. A, B FLAG-PIGL-associated proteins were identified using LC‒MS/MS (A) and ascertained by Co-IP (B). C Dual luciferase reporter assay. Five major transcription factors, p53, cMyc, HIF1α and RelA/B, were cotransfected with pGL3-response element and Renilla internal control plasmids into Hepa1-6 cells with or without PIGL overexpression. D ChIP‒qPCR assay. In Hepa1-6 cells with PIGL depletion or overexpression, an antibody against cMyc was used to enrich the corresponding DNA fragment. E, F Co-IP assay. In Hepa1-6 or H22 cells, PIGL was gradually expressed (E), and PIGL was depleted or overexpressed (F). An antibody against cMyc was used to enrich its associated complex. G In vitro pulldown assay. GST-tagged BRD4, cMyc and His-tagged PIGL were purified from E. coli and incubated together. Antibodies against His were used to enrich PIGL, and antibodies against GST were used to test the direct interaction between PIGL and cMyc or BRD4. H In vitro pulldown assay. GST-tagged cMyc, MBP-tagged BRD4 and His-tagged PIGL with gradually increasing levels were incubated together. Antibodies against GST were used to enrich cMyc, and antibodies against MBP or His were used to test the direct interaction between cMyc and BRD4 or PIGL. I In Hepa1-6 or H22 cells with PIGL depletion or overexpression, histone H3 acetylation at K9, K14 and K27 was detected. J ChIP‒qPCR assay. In Hepa1-6 or H22 cells with PIGL depletion or overexpression, an antibody against H3K27ac was used to enrich the corresponding DNA fragment. C One-way ANOVA; E, F, H, I Two-tailed Student’s t-test. (N.S., not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001)