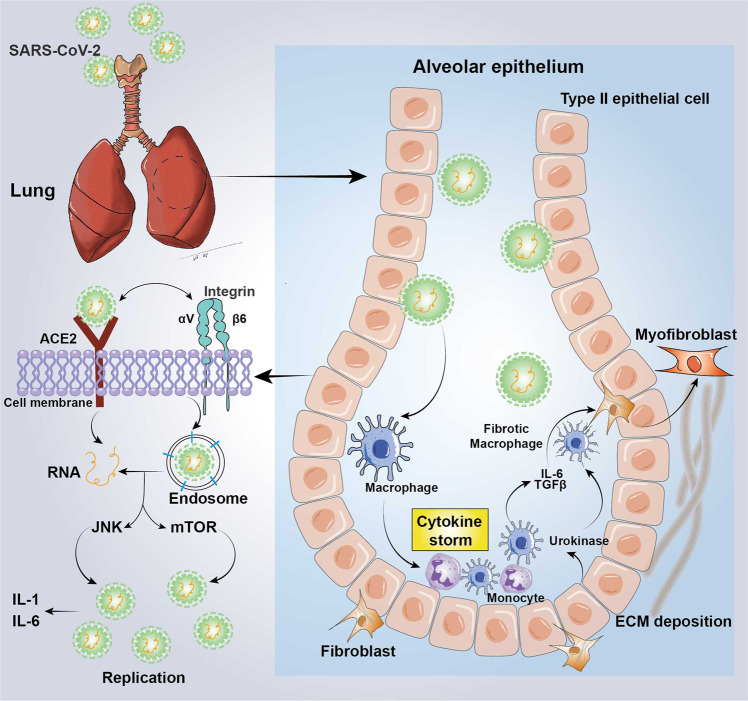
Fig. 7.
Biochemical mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2-induced lung fibrosis. SARS-CoV-2 initially binds to ACE2 of the epithelial cells to activate integrins or CD98. Integrins, especially αVβ6, can assist the SARS-CoV-2 binding to ACE2, thus enhancing the ability of viral infectivity. After SARS-CoV-2 is inhaled, the virus replicates through the JNK and mTOR signaling, which facilitate the generation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Meanwhile, the type II alveolar epithelium cell injury induces pro-inflammatory recruitment of immune cells, such as macrophages. The cytokine storm will then be released and triggers the proliferation and migration of fibroblasts. Besides, the activation of TGFβ triggered by integrins, IL-1, and IL-6 promotes ECM deposition and FMT. ACE2 angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, CAMK calmodulin kinase, SARS-CoV-2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, ECM extracellular matrix, FMT fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transformation, IL interleukin, TGFβ1 transforming growth factor β1