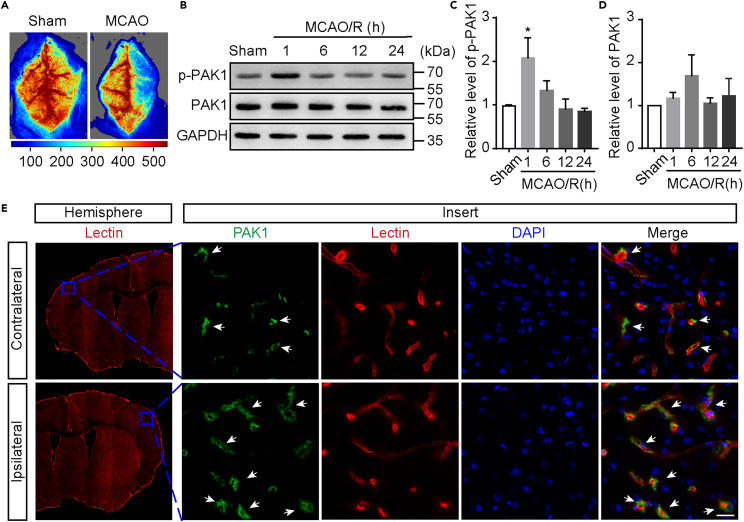
Figure 1.
Focal cerebral ischemia increases PAK1 phosphorylation
(A) Representative image of blood flow measured by laser speckle flowmeter.
(B) The time-dependent changes of PAK1 and p-PAK1 in ischemic cortex at 1 h, 6 h, 12 h, or 24 h reperfusion after 1-h transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). The homogenates of cortical brains from tMCAO and sham treated mice were subjected to Western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used as a loading control.
(C and D) The quantitative analysis of immunoblotted p-PAK1 (Ser144) and PAK1 proteins. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4). ∗p < 0.05 versus sham, one-way ANOVA with Dunnet’s post hoc test.
(E) Immunofluorescence images showing the colocalization of PAK1-positive (green) with microvessel markers Lectin (red) in the ipsilateral (I)/contralateral (C) cortex at 1 h reperfusion after tMCAO. White arrow shows that PAK1 is localized on blood vessels. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 20 μm.
See also Figure S1.