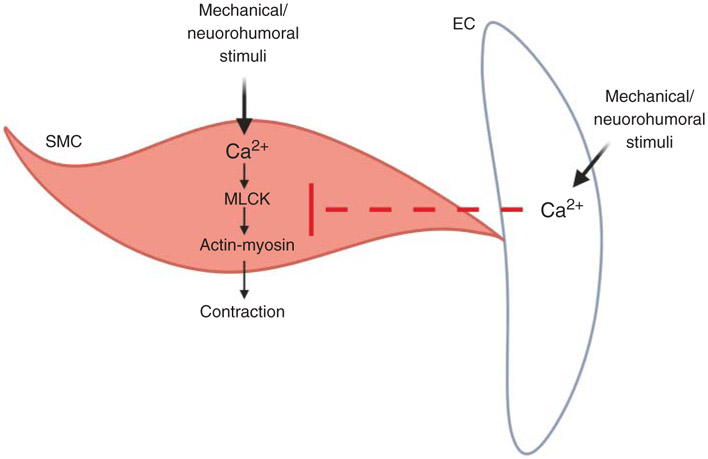
Figure 1. The contrasting effects of smooth muscle cell (SMC) and endothelial cell (EC) Ca2+ on vascular contractility.
Mechanical and neurohumoral stimuli can increase intracellular Ca2+ in SMCs and ECs. Intracellular Ca2+ in SMCs and ECs, in general, has opposite effects on vascular resistance. Increase in SMC Ca2+ activates the contractile machinery in SMCs (myosin light chain kinase or MLCK/Actin-Myosin). In contrast, an increase in EC Ca2+ inhibits SMC contractile mechanisms. The dotted red line indicates inhibition of SMC contractility.