Fig. 3.
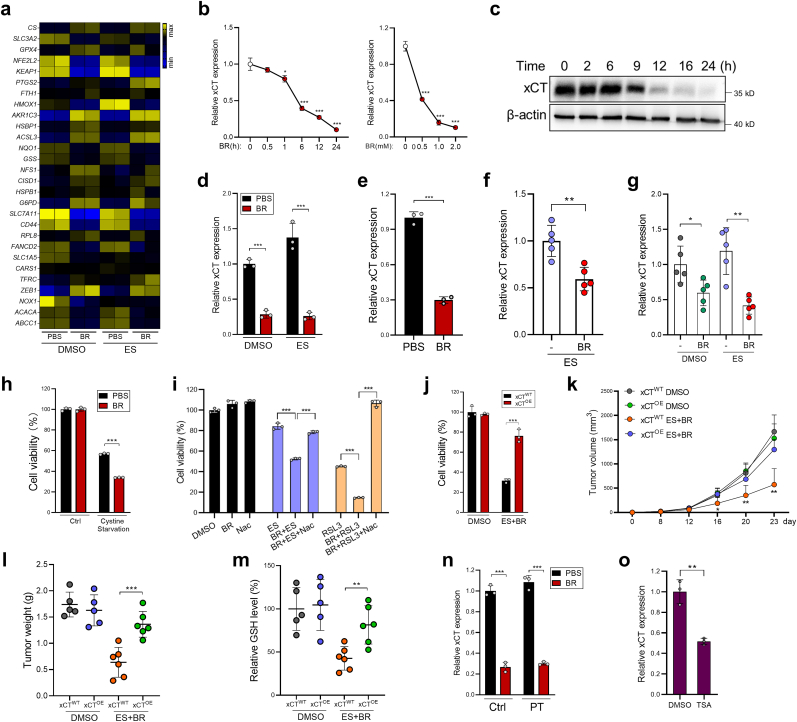
Butyrate inhibits xCT expression via HDAC inhibition. a, HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or erastin (20 μM) for 10 h in the presence or absence of butyrate (1 mM), then subjected to RNA-Seq. The expression levels of ferroptosis–related genes were shown. b,c HCT116 cells were treated with butyrate as indicated, xCT expression was evaluated by qPCR (b) and immunoblotting (c). d, Mouse CRC organoids were treated with butyrate; xCT expression was evaluated by qPCR. e, Organoids from CRC patients were stimulated with 1 mM butyrate for 12 h, xCT expression was evaluated by qPCR. f, g xCT expression in HCT116 tumors (f) and AOM/DSS tumors (g) were evaluated by qPCR. h, HCT116 cells treated with butyrate were cultured in cystine-sufficient or cystine-low conditions. Cell viability was evaluated by CCK8. i, HCT116 cells were treated with erastin (20 μM) or RSL3 (10 μM), either alone or in combination with butyrate in the absence or presence of NAC. Cell viability was evaluated by CCK8. j, xCTOE and control HCT116 cells were treated with a combination of butyrate + erastin. Cell viability was evaluated by CCK8. k, xCTOE or control HCT116 cells were inoculated s.c into nude mice, which were then treated with DMSO or butyrate + erastin (n = 5–6/group). Tumor growth was monitored. l, On day 23 mice were sacrificed and tumors were weighed. m, Tumor GSH levels were measured. n, HCT116 cells were pretreated with pertussis toxin (PT) for 2 h, followed by butyrate treatment for 12 h xCT expression was evaluated by qPCR. o, HCT116 cells were treated with TSA (10 mM). xCT expression was evaluated by qPCR. Data are represented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test.