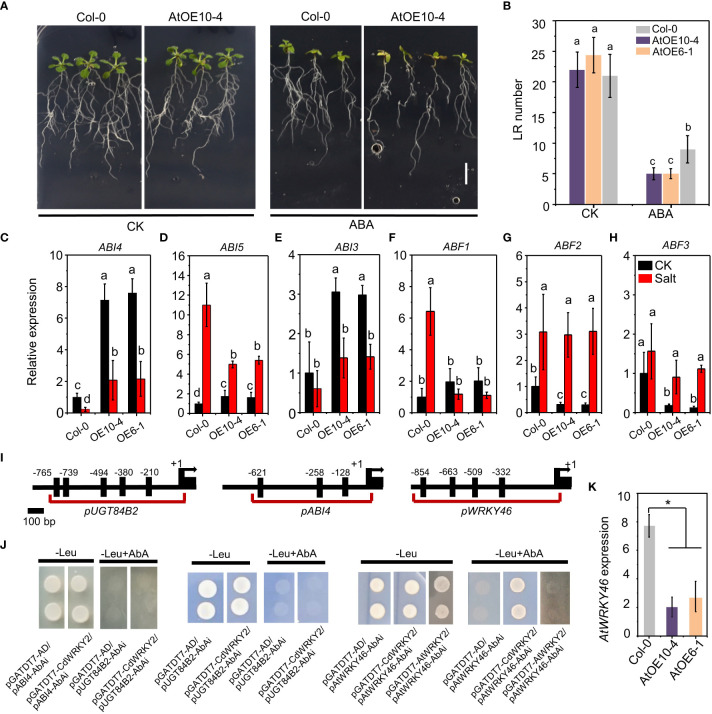
Figure 6.
The ABA sensitive phenotype of the CdWRKY2 overexpression Arabidopsis lines. The seeds of wild type (Col-0), CdWRKY2 overexpression lines (AtOE10-4 and AtOE6-1) were germinated for 4 days on 1/2 MS and the seedlings were then transferred to 1/2 MS containing 0 mM ABA (CK) or 10 μM ABA (ABA), respectively. After being grown vertically for 10 days, morphological parameters were measured. (A) Images of overexpression line (AtOE10-4) and wild type (Col-0) grown 10 days on CK and ABA conditions. Bar = 1 cm. (B) Visible LR number of overexpression lines and wild-type plants grown under CK and ABA conditions. (C–F) Relative expression of ABA-responsive genes in the roots of Col-0 and overexpression lines under control and salt conditions of three independent replicates. ABI4 (C), ABI5 (D), ABI3 €, ABF1 (F), ABF2 (G), ABF3 (H). UBQ10 was used as an internal control reference gene. Transcript levels of each sample were normalized to the expression of untreated wild-type plants. Three independent replicates were performed. Two-way ANOVA test was used and the data were further compared by Tukey’s post‐hoc test. Different letters on histograms indicate that means were statistically different at the p < 0.05 level. (I) Illustration of the ABI4, UGT84B2, and AtWRKY46 promoter regions showing the presence of consensus motif W-box. Shown are 2-kb upstream sequences of genes. (J) Yeast one-hybrid analysis of the binding of CdWRKY2 to the promoters. The promoter region of ABI4, UGT84B2, and AtWRKY46 containing multiple W-box was constructed into pAbAi vector, respectively, and was used to check DNA binding activity of CdWRKY2 using yeast one-hybrid method. The promoter region of AtWRKY46 was then used to check the DNA binding activity of AtWRKY2. (K) The relative expression level of AtWRKY46 in CdWRKY2 overexpression lines. Data are represented as means ± SD of three independent replicates, and * indicates significant difference between Col-0 and overexpression lines at p < 0.05 by one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s post‐hoc test.