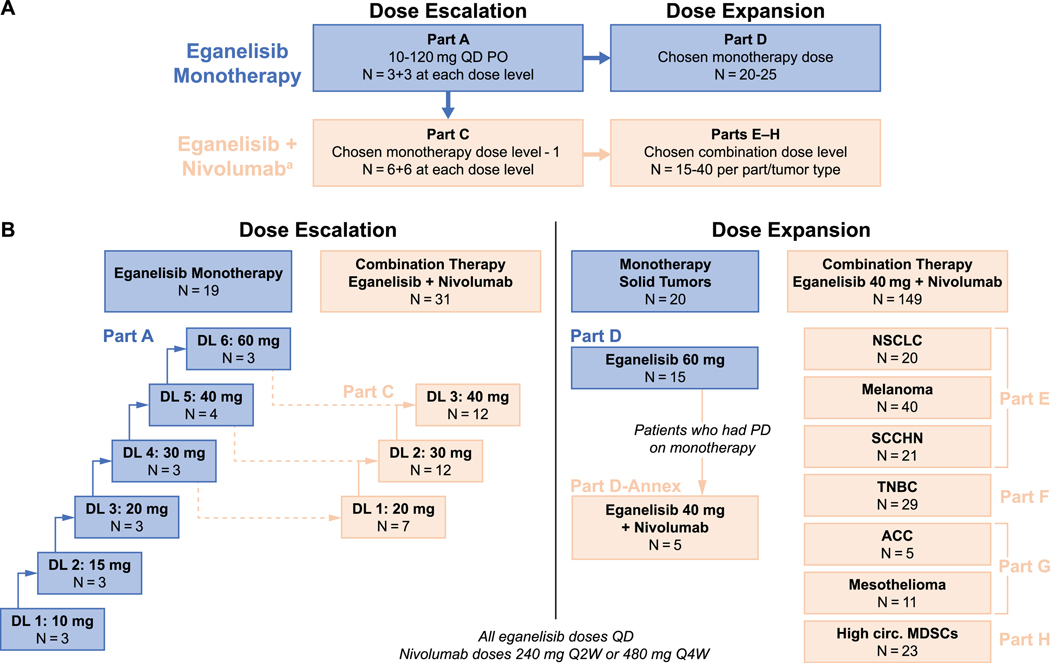
Figure 1. Study design and patient flow.
A) Study schema showing eganelisib dosing and numbers of patients planned for dose escalation and dose expansion cohorts. B) Numbers of patients enrolled at each dose level.
Abbreviations: ACC, adrenocortical carcinoma; DL, dose level; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; PD, progressive disease; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; PO, oral route; Q2W, every 2 weeks; Q4W, every 4 weeks; QD, once daily; SCCHN, squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer.
Part B (examining twice daily dosing) was planned if pharmacokinetic data indicated that QD dosing did not result in adequate eganelisib exposure. It was determined that Part B was not necessary, and it was not conducted. Part I, which was originally designed to evaluate patients with cisplatin-refractory, anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy-naïve advanced urothelial cancer receiving eganelisib in combination with nivolumab, was not conducted.
aNivolumab was administered at 240 mg Q2W or 480 mg Q4W per Investigator discretion.