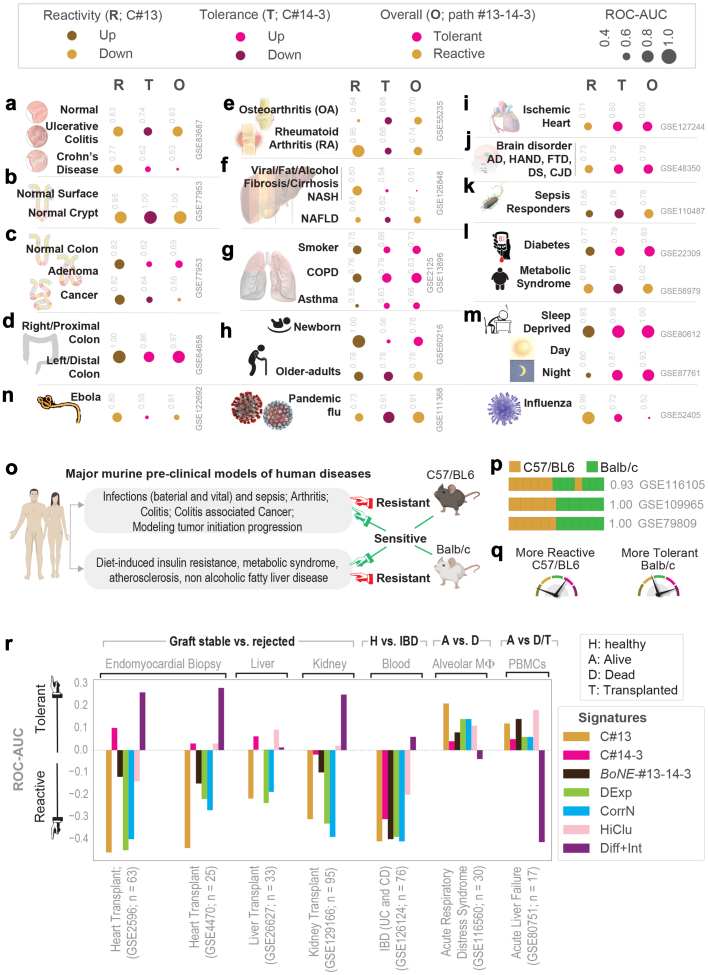
Fig. 3.
Definitions of “reactivity” and “tolerance” detects pathologic macrophage states in disease. Tissue immune microenvironment is visualized (in panels a–n) as bubble plots of ROC-AUC values (radii of circles are based on the ROC-AUC; Key on top) demonstrating the direction of gene regulation (Up vs Down; Key on top) for the classification of samples using BoNE-derived gene signatures of either reactive (R; C#13) or tolerant (T; C#14-3) or overall (O; path #13 → 14 → 3) in columns. The ROC-AUC values are provided next to the bubble. Sample diversity and sizes are as follows: a) IBD; GSE83687, n = 134; 60 Normal, 32 Ulcerative Colitis, 42 Crohn’s Disease. b) Colon crypt; GSE77953, 6 Normal Surface vs 7 Normal Crypt base. c); Colon cancer: Pooled colon dataset from NCBI GEO; n = 170 Normal, 68 Adenomas, 1662 CRCs. d) Colon anatomy: Proximal (right) vs distal (left) normal colon from mouse (GSE64423, n = 6) and human (GSE20881, n = 75). See Supplementary Fig. S7 for violin plots. e) Arthritis; GSE55235, GSE55457 and GSE55584, n = 79; 20 Normal, 33 Rheumatoid Arthritis, 26 Osteoarthritis. f) Hepatitis: GSE89632, n = 63; 20 fatty liver, 19 Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and 24 healthy, alcoholic liver disease (GSE94417, GSE94397 and GSE94399, n = 195; 109 Healthy, 13 Alcoholic Hepatitis, 6 Alcoholic fatty liver (AFL), 67 Alcoholic cirrhosis (AC) and viral hepatitis (GSE70779, n = 18; 9 Pre-treatment, 9 Post-treatment with direct-acting anti-virals). g) Chronic lung disease; GSE2125 and GSE13896, n = 115; 39 Non-smoker, 49 Smoker, 15 Asthma, 12, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). h) Aging process; GSE60216, n = 9; 3 Newborn babies, 3 Adults, 3 Old-adults. i) Cardiomyopathy (CM), ischemic and non-ischemic (I/NI); GSE104423, n = 25 human samples; 14 NICM, 11 ICM; GSE127244, n = 24 mouse samples, 16 NICM, 8 ICM. j) Neurodegenerative brain disorders; GSE118553 (n = 401) and GSE48350 (n = 253), Alzheimer’s disease (AD); GSE35864, HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND; n = 72); GSE13162, frontotemporal dementia (FTD; n = 56); GSE59630, Down’s Syndrome (DS; n = 116); GSE124571, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD; n = 21). k) Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and sepsis; GSE63042 (n = 129); GSE110487 (n = 31). l) Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome; GSE22309 (n = 110), Pre- and post-insulin treatment muscle biopsies from 20 insulin sensitive, 20 insulin resistant, 15 T2DM; GSE98895 (n = 40), PBMCs from 20 control, 20 metabolic syndrome. m) Sleep deprivation and circadian rhythm; GSE9444, n = 131 mouse brain and liver samples; GSE80612, twin, n = 22 human peripheral blood leukocytes; GSE98582, n = 555 human blood samples; GSE104674, n = 48, 24 healthy and 24 T2DM. n) Viral pandemics, such as SARS, MERS, Ebola, and others [see Supplementary Fig. S9E]. See Supplementary Fig. S8 for violin plots relevant to panels e–j. See Supplementary Fig. S9 for violin plots relevant to k–m. o–q) Schematic (o) summarizes the use of two major mouse strains (C57/B6 and Balb/c) commonly used for modeling two broad categories of human diseases. Bar plots (p) showing sample classification of genetically diverse macrophage datasets based on expression levels of genes in C#13. Schematic (q) summarizes findings. r) The diagnostic potential of various indicated gene signatures were tested on multiple datasets generated from tissues derived from patients with the known clinically relevant outcome, as indicated. In each case, BoNE-derived signatures were compared against four traditional approaches.