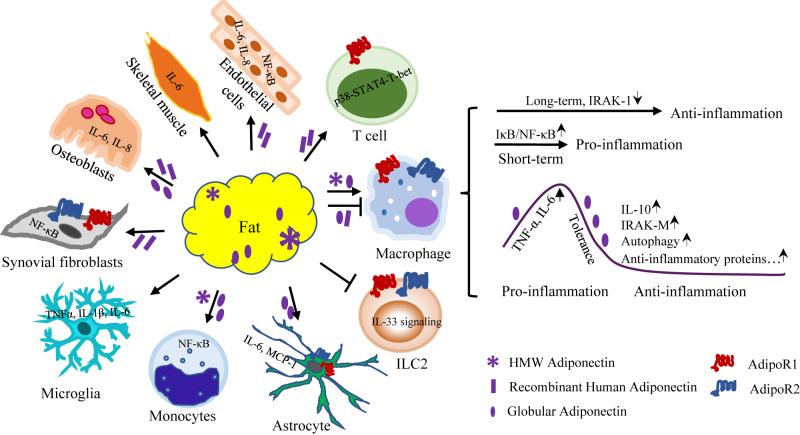
Figure 2:
Pro-inflammatory properties of adiponectin under certain circumstances. Adiponectin level in circulation is positively correlated with a number of inflammatory disorders such as preeclampsia, rheumatoid arthritis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. αUnder certain circumstances, adiponectin induces the expression of inflammatory mediators in skeletal muscle, immune cells and non-immune cells, via various mechanisms. In macrophage, adiponectin acts as anti- and pro-inflammatory factor, which is mediated by its initial induction on inflammatory response and the subsequent tolerance to its own stimulation and/or to other pro-inflammatory signals. NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-8, interleukin-8; IL-10, interleukin-10; IL-33, interleukin-33; ILC2, group 2 innate lymphoid cells; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IRAK-1, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1. ↑ refers to increase, while ↓ means decrease.