Figure 1. Diagram of the Me31B wildtype and mutant proteins in the Drosophila strains generated in this study.
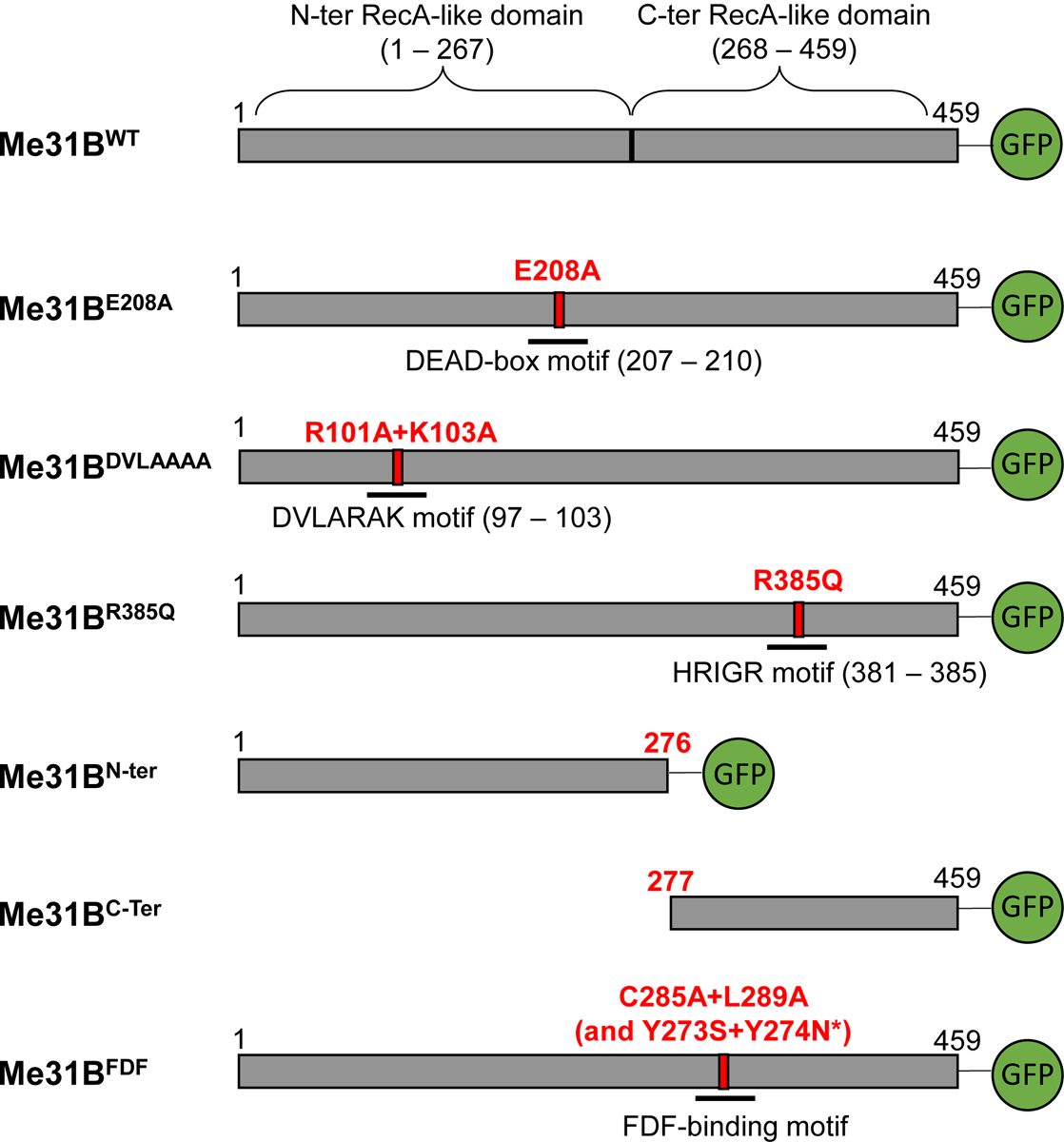
The bar after each Me31B protein name represents the primary structure of the protein. The numbers on top of the bars mark the number of amino acids and their positions in the protein. Green Fluorescence Protein (GFP) tags are expressed at the C-terminal end of the constructed Me31B proteins. The point mutations are as follows: E208A, glutamic acid 208 replaced by alanine; R101A, arginine 101 replaced by alanine; K103A, lysine 103 replaced by alanine; R385Q, arginine 385 replaced by glutamine; C285A, cysteine 285 replaced by alanine; L289A, leucine 289 replaced by alanine; Y273S, tyrosine 273 replaced by serine; Y274N, tyrosine 274 replaced by asparagine. Me31BN-ter protein (deletion of amino acids 277 to 459) contains the first 276 amino acids of the wild-type protein. Me31BC-ter protein (deletion of amino acids 1 to 276) contains the last 183 amino acids of the wild-type protein.
*Note that two unintended, missense mutations were detected in the me31BFDF strain when sequencing its me31B gene. The two mutations (Y273S and Y274N) are outside the FDF-binding motif.
