Figure 2.
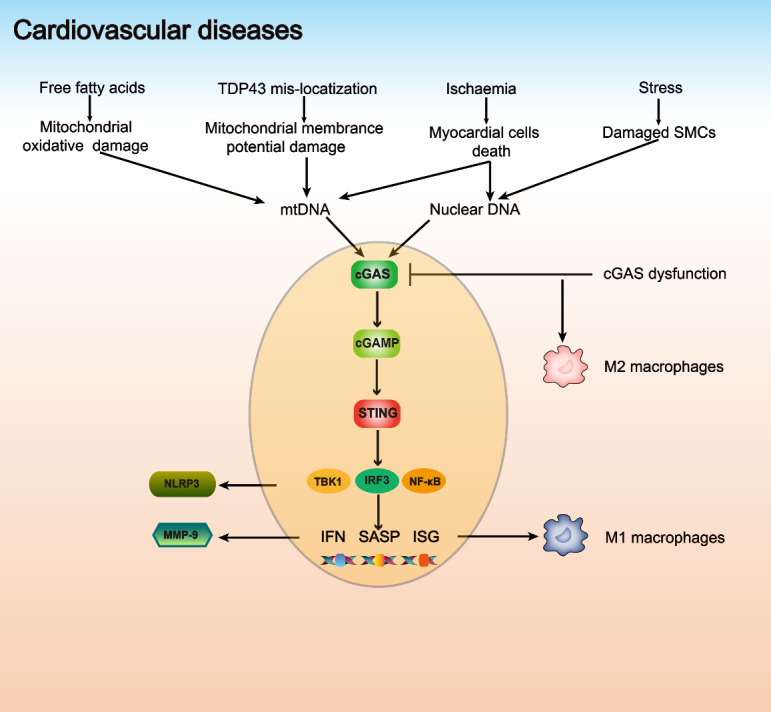
The cGAS-STING pathway in cardiovascular diseases. Free fatty acids can cause mitochondrial oxidative damage, and TDP43 mislocalization results in mitochondrial potential damage. This damage to mitochondria leads to the leakage of mtDNA into the cytoplasm. Damaged SMCs and myocardial cells release nuclear DNA; in addition, dead myocardial cells release mtDNA into the cytoplasm due to ischemia. This cytosolic dsDNA activates the cGAS-STING pathway and induces the production of NLRP3, MMP-9 and M1 macrophages (proinflammatory and antimicrobial), and inhibition of cGAS promotes the formation of M2 macrophages (healing, profibrotic, and anti-inflammatory).
