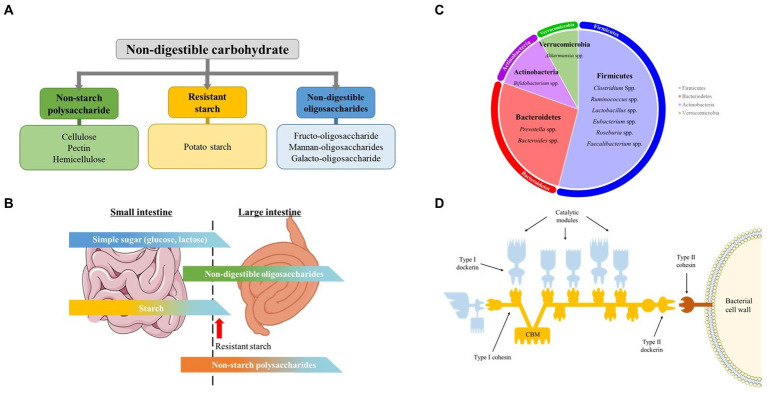
Figure 1.
Non-digestible carbohydrates, pig gut microbiome, carbohydrate digestion in the intestine, and celluosome structure. (A) Classification and examples of non-digestible carbohydrate addressed in this mini review. (B) Schematic illustration of digestion of different carbohydrates in small and large Intestine. The figure gives a rough idea on the amount of carbohydrates digested in the small and large intestine. Modified from Bach Knudsen et al. (C) Predominant genus of swine gut microbiota. Each area of the circle signifies the domination of the respective phyla in the swine gut. (D) Cellulosome structure. The Type I dockerins, attached to the catalytic subunit (blue) interacts with the cohesin (yellow) of the primary CipA scaffoldin protein forming cellulosome complex. The cellulosome is attached to the bacterial surface through interaction of Type II dockerin in CipA with Type II cohesin module of a membrane-bound protein (red). The Cellulosome complex binds to cellulose through cellulose-binding module (CBM) of the CipA primary scaffoldin protein. Modified from Gilbert H.J.