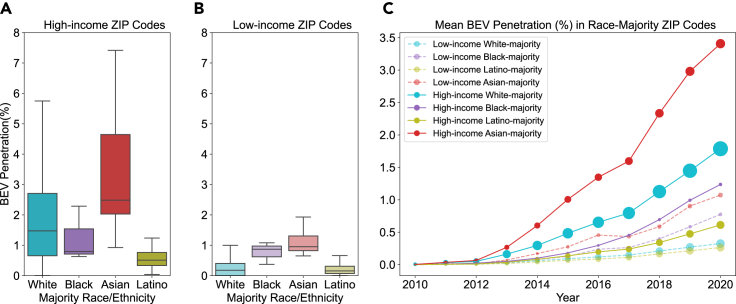
Figure 1.
BEV penetration in high- and low-income ZIP codes with racial and ethnic majorities
(A) BEV penetration in 2020 in high-income racial and ethnic-majority ZIP codes. Statistical significance of the difference between medians is as follows: White vs. Black: ∗∗∗; White vs. Asian: ∗∗∗∗; White vs. Latino: ∗∗∗∗; Black vs. Asian: ∗∗∗∗; Black vs. Latino: ∗∗; Asian vs. Latino: ∗∗∗∗. ns = no statistical significance, ∗ = p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗ = p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗ = p ≤ 0.001, ∗∗∗∗ = p ≤ 0.0001. The midline indicates the median, the upper and lower edges of the box indicate the upper and lower quartiles, and the whiskers indicate the minimum and maximum values excluding outliers.
(B) BEV penetration in 2020 in low-income racial and ethnic-majority ZIP codes. Statistical significance of the difference between medians is as follows: White vs. Black: ∗; White vs. Asian: ∗∗∗∗; White vs. Latino: ∗∗∗∗; Black vs. Asian: ∗∗∗∗; Black vs. Latino: ∗∗∗; Asian vs. Latino: ∗∗∗∗. ns = no statistical significance, ∗ = p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗ = p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗ = p ≤ 0.001, ∗∗∗∗ = p ≤ 0.0001. The midline indicates the median, the upper and lower edges of the box indicate the upper and lower quartiles, and the whiskers indicate the minimum and maximum values excluding outliers.
(C) Mean BEV penetration in ZIP codes in each racial/ethnic and income category from 2010 to 2020.