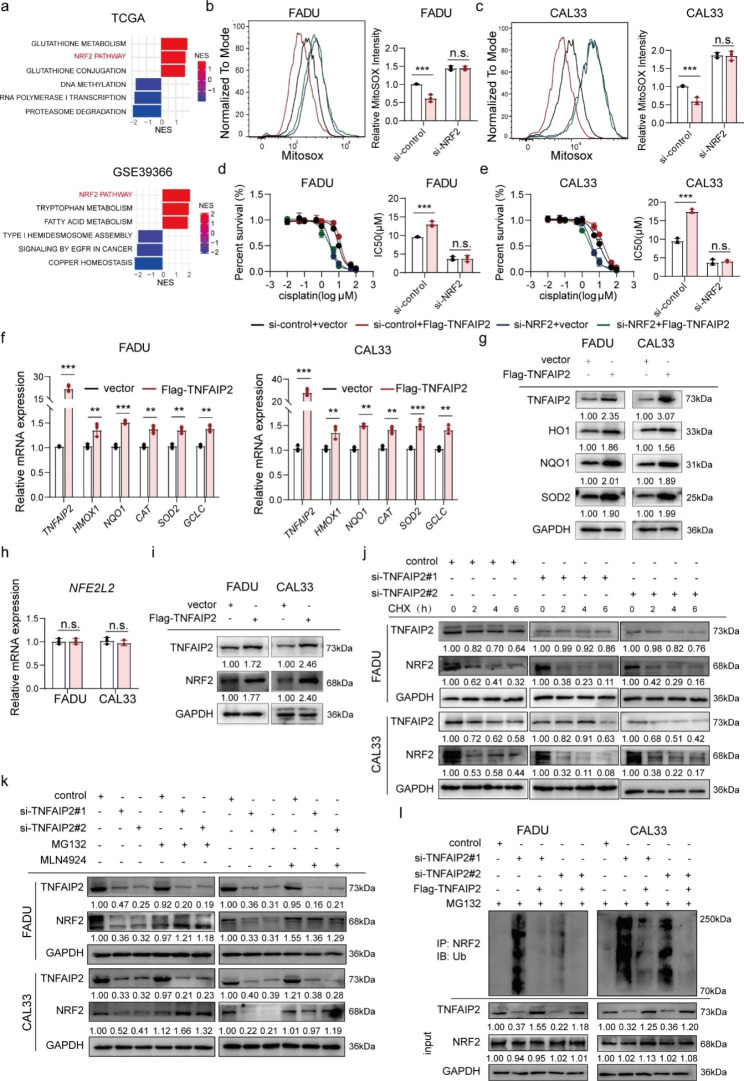
Fig. 3.
TNFAIP2 stabilizes the NRF2 protein by inhibiting its ubiquitination degradation. (a) GSEA of signaling pathways significantly correlated with TNFAIP2 in TCGA-HNSCC and GSE39366. (b-c) Flow cytometry analyses of ROS in TNFAIP2-overexpressing FADU (b) and CAL33 (c) cells with or without NRF2 knockdown. (d-e) Cisplatin IC50 evaluations in TNFAIP2-overexpressing FADU (d) and CAL33 (e) cells with or without NRF2 knockdown. (f-g) The mRNA (f) and protein (g) levels of NRF2 target genes in TNFAIP2-overexpressing HNSCC cell lines. (h-i) The mRNA (h) and protein (i) levels of NRF2 in TNFAIP2-overexpressing HNSCC cell lines. (j) The NRF2 protein level in TNFAIP2 knockdown HNSCC cell lines treated with CHX (50 µg/ml) at the corresponding time points. (k) The NRF2 protein level in TNFAIP2 knockdown HNSCC cell lines treated with or without MG132 (10 µM, 4 h) or MLN4924 (2 µM, 1 h). (l) Co-IP analyses of NRF2 ubiquitination in HNSCC cell lines with the indicated treatments treated with MG132 (10 µM, 4 h). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. n.s., not significant; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001. GSEA, gene set enrichment analysis