FIGURE 4.
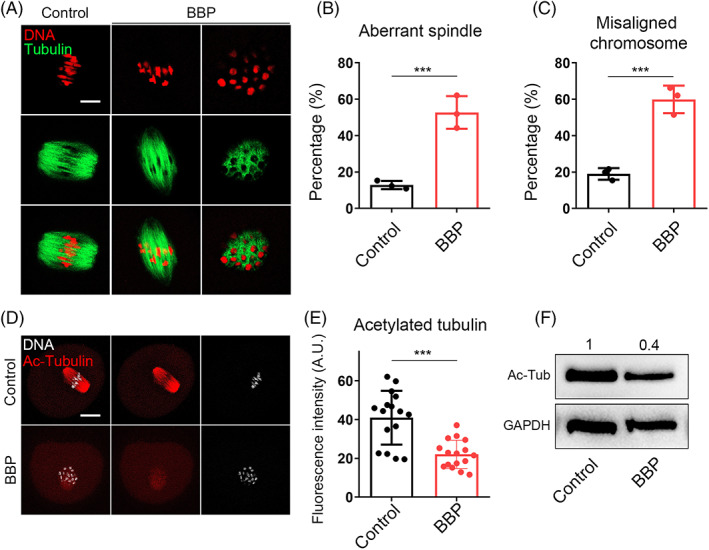
Benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) exposure leads to spindle/chromosome disruption and decreased ac‐tubulin levels in mouse oocyte. (A) Representative images of spindle and chromosome in the MI oocyte from control and BBP‐exposed groups. Green, α‐tubulin; red, DNA. (B) The percentage of MI oocytes with aberrant spindle in BBP‐exposed group was significantly higher than that in the control group. Results are expressed as mean ± SD; experiments were repeated at least three times (NS, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). (c) The percentage of MI oocytes with misaligned chromosome in BBP‐treated group was significantly higher than that in the control group. Results are expressed as mean ± SD; experiments were repeated at least three times (NS, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). (D) Representative images of ac‐tubulin in the control and BBP‐exposed groups. Red, ac‐tubulin; grey, DNA. (E) The fluorescence intensity of ac‐tubulin in BBP‐exposed oocytes was much lower than that in the control oocytes. Results are expressed as mean ± SD; experiments were repeated at least three times (NS, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). (F) Western blot result also displayed a declined level of ac‐tubulin. K‐M, kinetochore–microtubule.
