FIGURE 5.
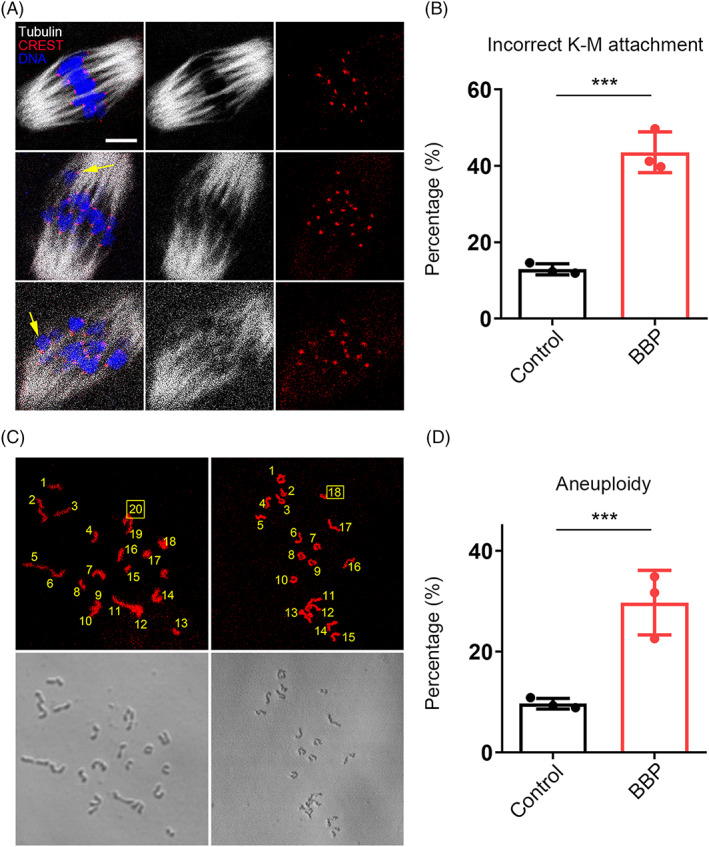
Benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) exposure leads to defective kinetochore–microtubule (K‐M) attachment and aneuploidy in mouse oocyte. (A) Representative images of the morphology of K‐M attachments in MI oocytes from both control and BBP‐exposed group. Grey, α‐tubulin; red, CREST; blue, DNA. (B) The rate of incorrect K‐M attachment in BBP‐exposed group was significantly higher than that in control group. Results are expressed as mean ± SD; experiments were repeated at least three times (NS, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). (C) Representative images of the number of chromosomes through chromosome spreading on MII oocytes in each group. Red, DNA. (D) Aneuploidy in BBP‐exposed group was prominently increased comparing with that in the control group. Results are expressed as mean ± SD; experiments were repeated at least three times (NS, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).
