Figure 2. Effects of STAT4 Variants on Phosphorylation.
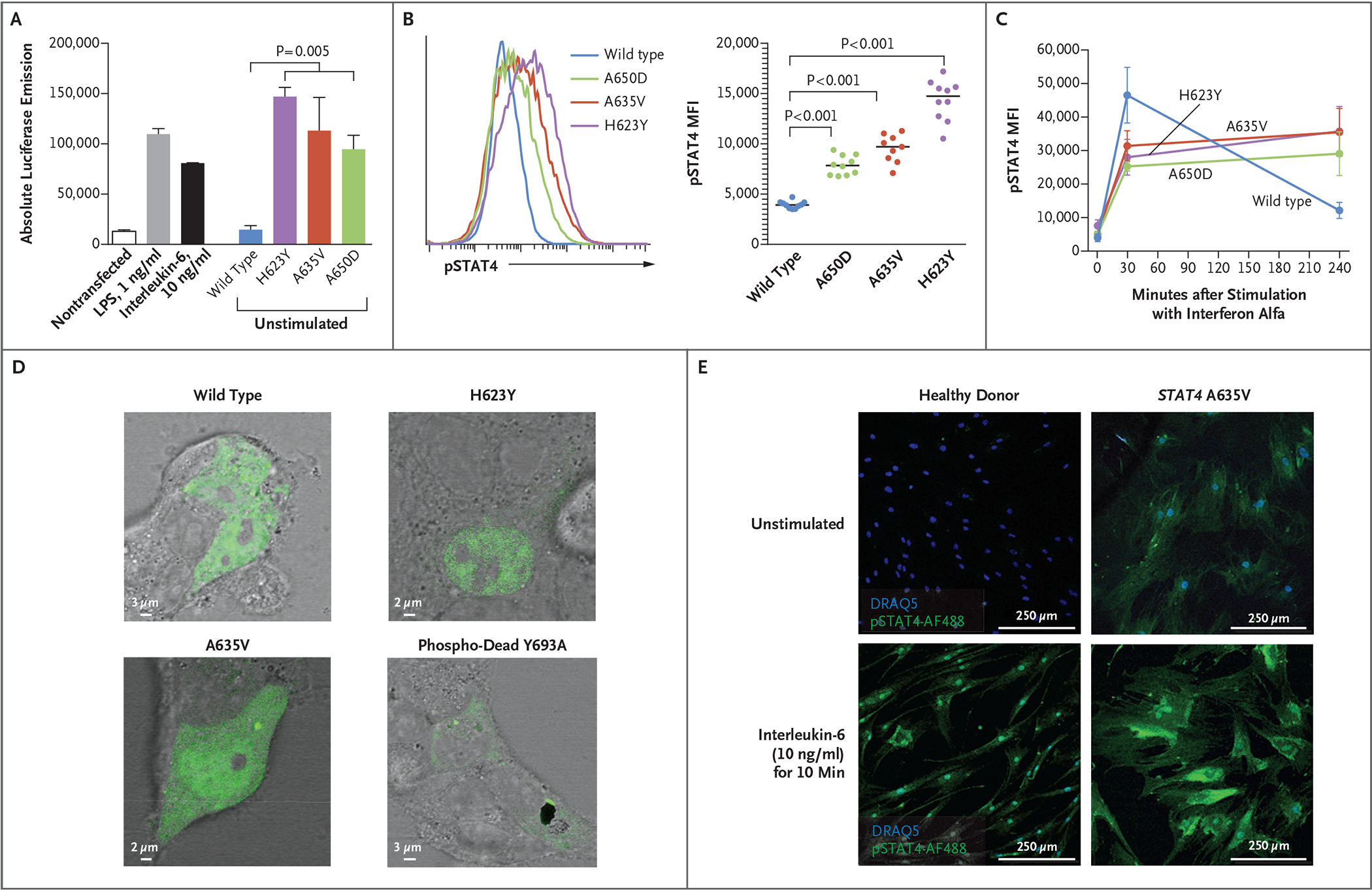
Panel A shows absolute luciferase emission from the interleukin-6 Leeporter cell line transfected with vector carrying wild-type or variant STAT4. Transcriptional activity was enhanced in the presence of STAT4 A635V, H623Y, and A650D, as compared with wild-type STAT4 and the nontransfected cell line, with or without stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or interleukin-6. Panels B and C show STAT4 phosphorylation in U3A cells stably transfected with wild-type or variant STAT4. Flow cytometry that was used to measure the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of phosphorylated STAT4 (pSTAT4) showed increased pSTAT4 in unstimulated cells (Panel B) that were transfected with A635V (red), A650D (green), and H623Y (purple) variants, as compared with wild-type STAT4 (blue). In response to interferon alfa (Panel C), STAT4 phosphorylation persisted in variant cells at 240 minutes as compared with wild-type cells. In Panels A and C, error bars indicate standard errors. Panel D shows HEK293T cells transiently transfected with plasmids containing wild-type, H623Y, A635V, or phospho-dead Y693A STAT4 tagged with green fluorescent protein. Unstimulated cells that were transfected with H623Y or A635V variants had a greater accumulation of STAT4 in the nucleus than those transfected with wild-type or Y693A STAT4. Panel E shows that primary skin fibroblasts from a patient with the A635V variant had prominent pSTAT4 (green), as compared with fibroblasts from a healthy donor. Phosphorylated STAT4 staining of patient fibroblasts persisted in a perinuclear location with interleukin-6 stimulation. Nuclear staining was performed with DRAQ5 (blue).
