Figure 3. Evaluation of the Function of Primary Skin Fibroblasts In Vitro.
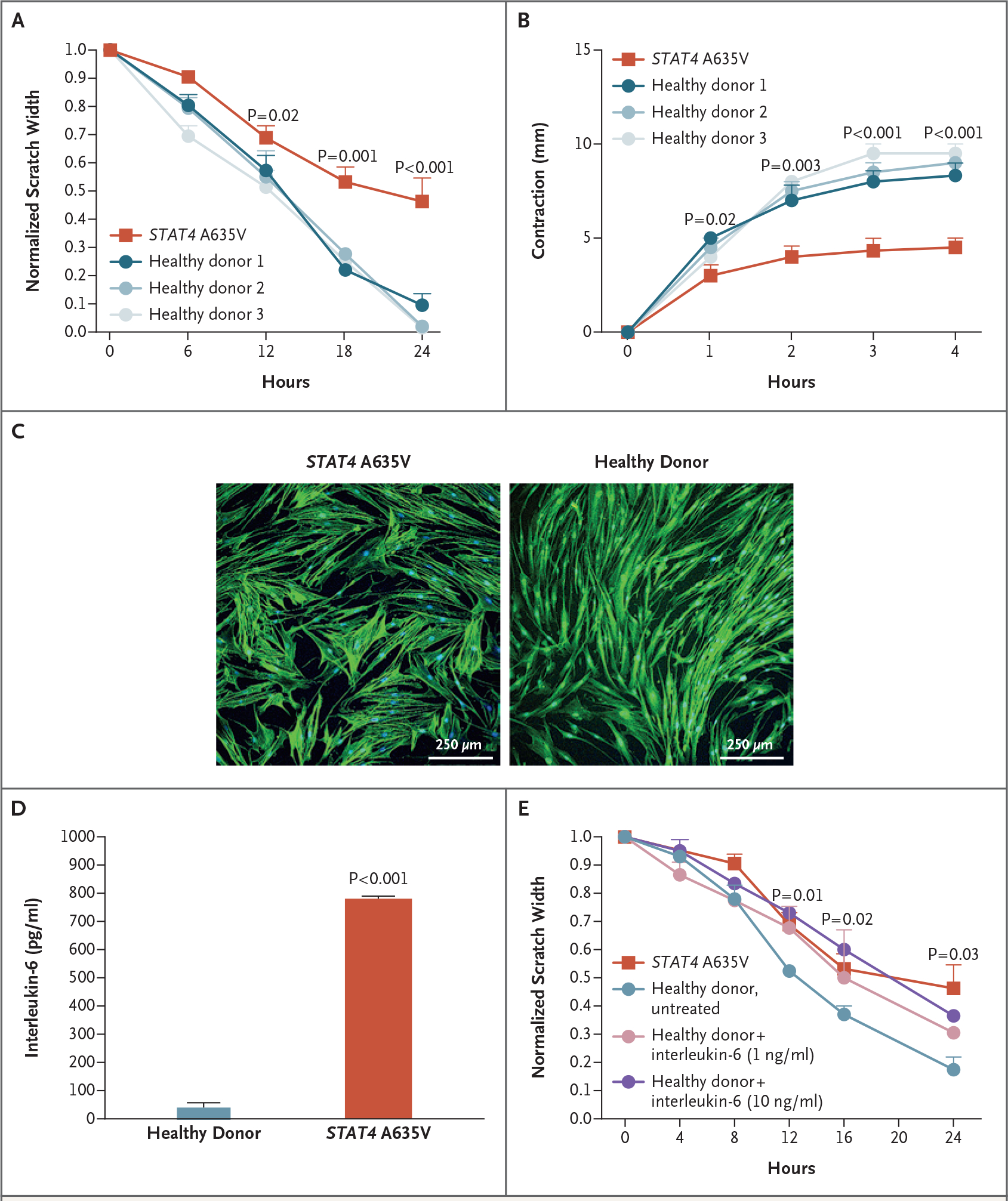
Panel A shows that wound healing as measured by scratch assay was reduced in fibroblasts from patients with STAT4 A635V (red), as compared with fibroblasts from healthy donors (blue). For the scratch assays, three experiments were performed with six scratches each. Panel B shows that transforming growth factor β–induced contraction of collagen matrix by patient-derived fibroblasts (red) was reduced relative to fibroblasts from healthy donors. Panel C shows that in F-actin immunocytochemical analysis, cell size was increased in primary skin fibroblasts from a patient with STAT4 A635V, as compared with fibroblasts from healthy donors. Panel D shows that patient fibroblasts had enhanced interleukin-6 secretion in the absence of stimulation. Panel E shows that wound healing was reduced in primary skin fibroblasts from healthy donors when treated with varying concentrations of interleukin-6, with rates approaching those of cells from patients with STAT4 A635V (three experiments with six scratches each). Throughout the figure, P values were calculated by means of two-way analysis of variance. Error bars indicate standard errors.
