Figure 4. Janus Kinase Inhibition, Reduction of STAT4 Phosphorylation, and Wound Healing.
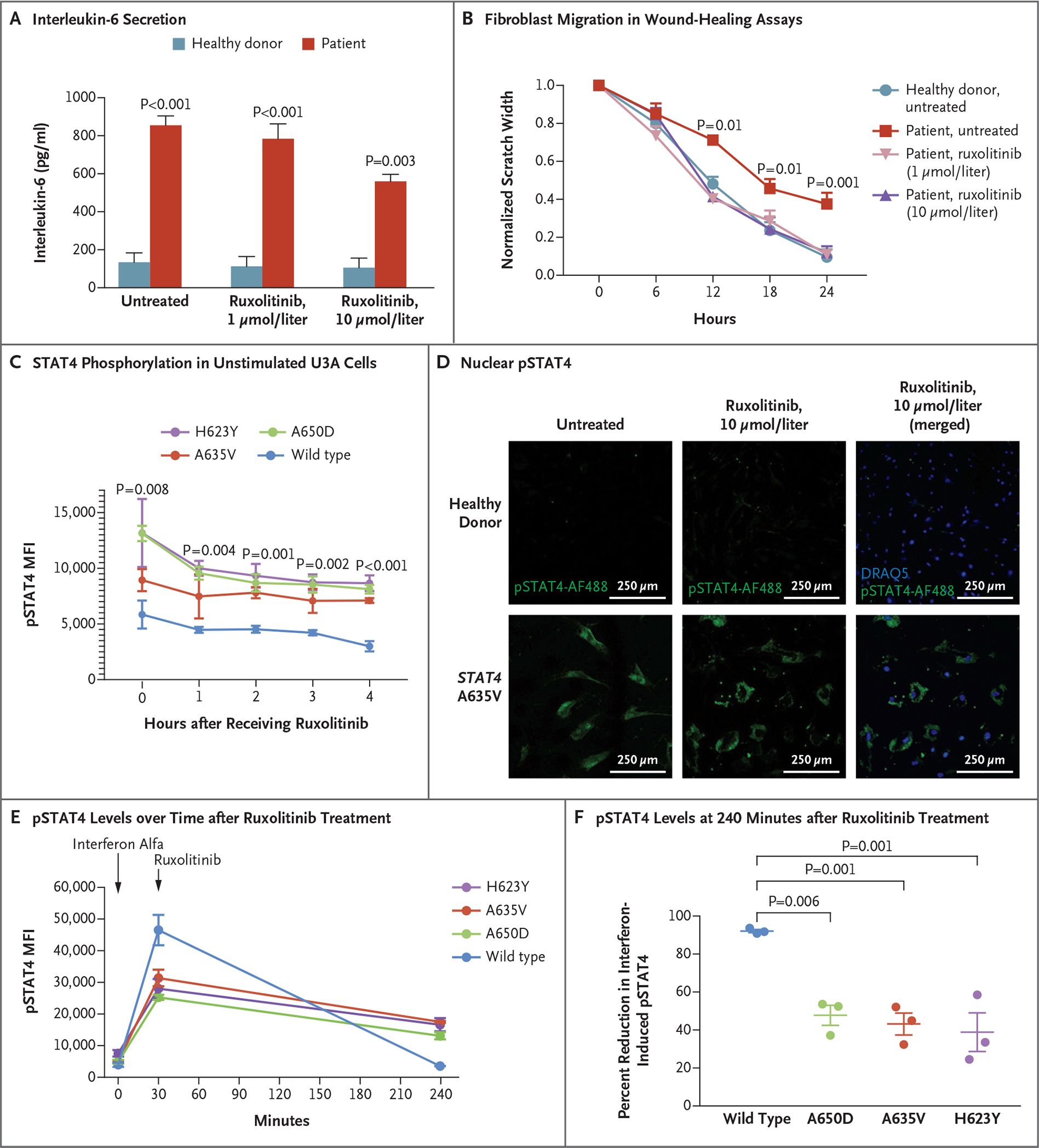
Panel A shows that patient fibroblasts had enhanced interleukin-6 secretion that was responsive to ruxolitinib. Data for healthy donors are a summary of three such donors. The P value for patient cells treated with ruxolitinib as compared with untreated patient cells is 0.02. Panel B shows that pretreatment with ruxolitinib led to enhanced fibroblast migration in wound-healing assays, with closure at 24 hours that was similar to that in unaffected fibroblasts (three experiments with six scratches each). Panel C shows that STAT4 phosphorylation in unstimulated U3A cells was reduced after treatment with ruxolitinib. Panel D shows that nuclear pSTAT4 was reduced in response to ruxolitinib treatment of patient fibroblasts. Panels E and F show that interferon alfa–stimulated U3A cells expressing variant STAT4 had higher levels of pSTAT4 than cells expressing wild-type STAT4 at 240 minutes. Ruxolitinib treatment decreased phosphorylation in cell lines expressing variant STAT4 and in those expressing wild-type STAT4. In Panel F, mean decreases and standard errors are shown. Throughout the figure, P values were calculated by means of two-way analysis of variance. Error bars indicate standard errors.
