Fig. 3.
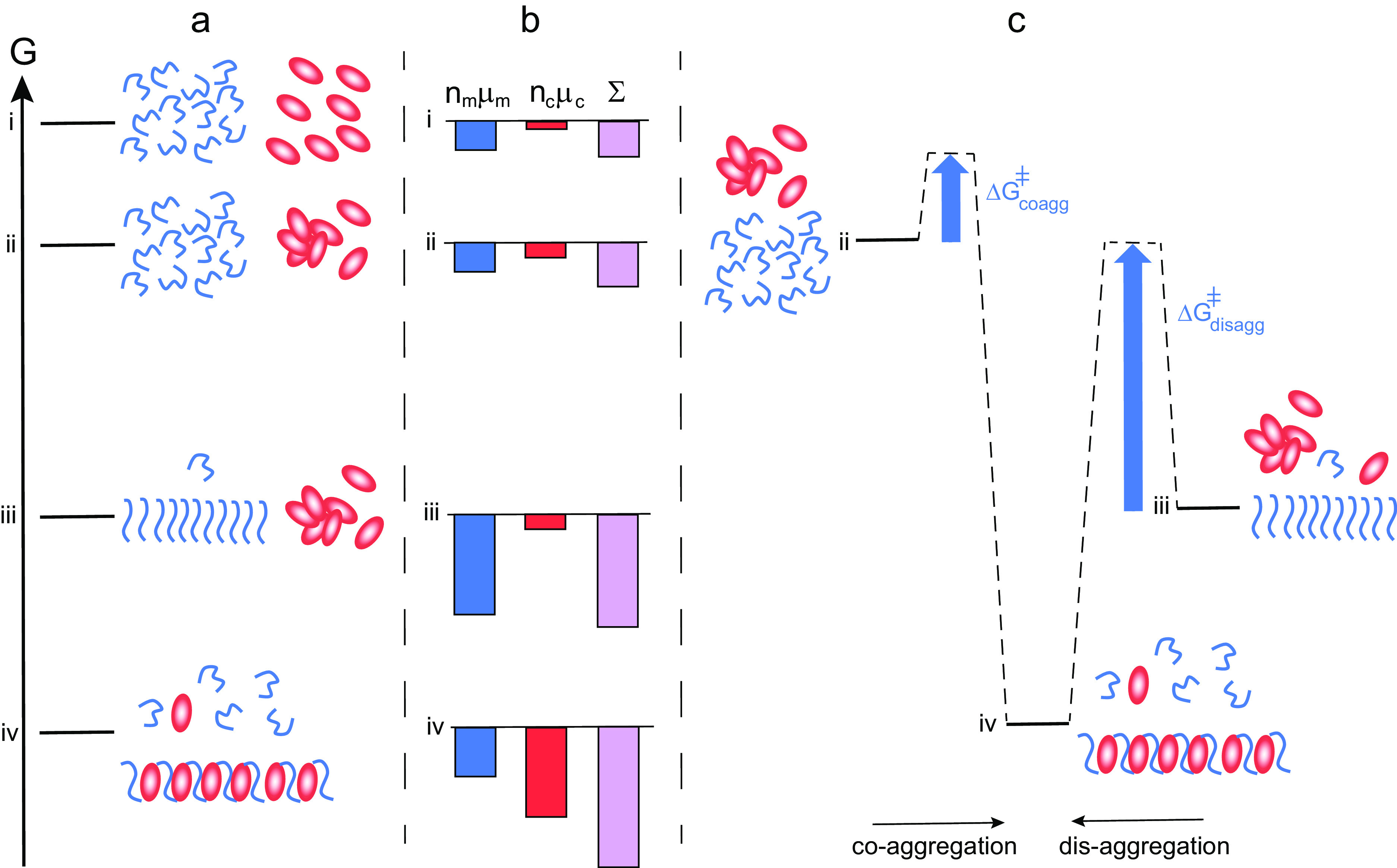
Thermodynamics of co-aggregation and disaggregation. (a) Free energy diagram for a closed system of an amyloid peptide (blue) and chaperone (red). At the highest level i, all species are monomeric. At level ii, the peptide is monomeric and the chaperone a mixture of monomers and oligomers. At level iii, there are amyloid fibrils, chaperone oligomers and monomers of both. At level iv, co-aggregates of peptide and chaperone co-exist with monomers of both, and the peptide monomer concentration in this state is higher than in state iii. (b) Chemical potential summed up over all molecules of each kind separately (peptide blue and chaperone red), and for the system (purple). There is a large increase in amyloid peptide solubility from state iii to state iv. (c) Reaction coordinate diagram for the case of co-aggregation (from ii to vi) and for disaggregation (from iii to iv) illustrating the much higher energy barrier in the latter case.
