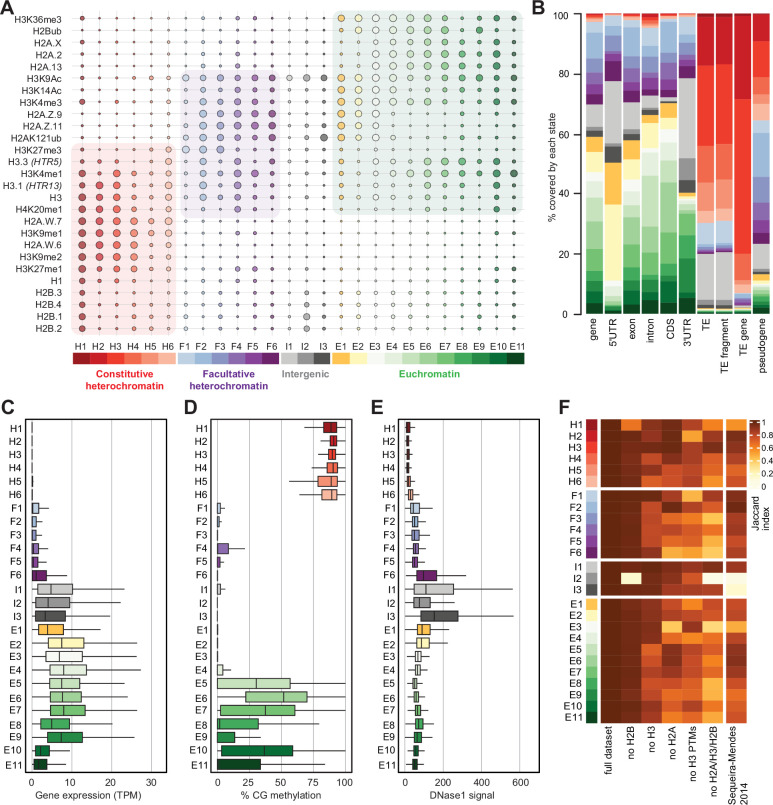
Figure 2. Histone variants define chromatin states in Arabidopsis thaliana.
(A) Bubble plot showing the emission probabilities for histone modifications/variants across the 26 chromatin states. (The size of the bubble represents the emission probability ranging from 0 to 1). The colors are ascribed for each type of chromatin. (B) Stacked bar plot showing the overlap between annotated genomic features and chromatin states. (C) Box plot showing the expression of protein-coding genes overlapping with each chromatin state in Transcripts per Million (TPM). (D) Box plot showing levels of CG methylation across chromatin states. (E) Box plot comparing DNase I-seq read coverage across chromatin states representing chromatin accessibility. (F) Heatmap showing the Jaccard similarity index between the states generated using the whole model and states using a subset of marks, i.e., excluding a set of marks and variants as indicated on the x-axis. The comparison with a 9-state model (Sequeira-Mendes et al., 2014) did not include CG content, DNA methylation, H4K5ac, and H3K4me2 which were not used in the 26-state model. H2B did not seem to make a significant contribution. Excluding H3 did reduce effectively the Jaccard index for both the 26 and the 9 chromatin states model, which both included H3.1 and H3.3. The major differences between the 26 and the 9 chromatin states model are in the intergenic states. Overall H2A variants affected most strongly the Jaccard index.