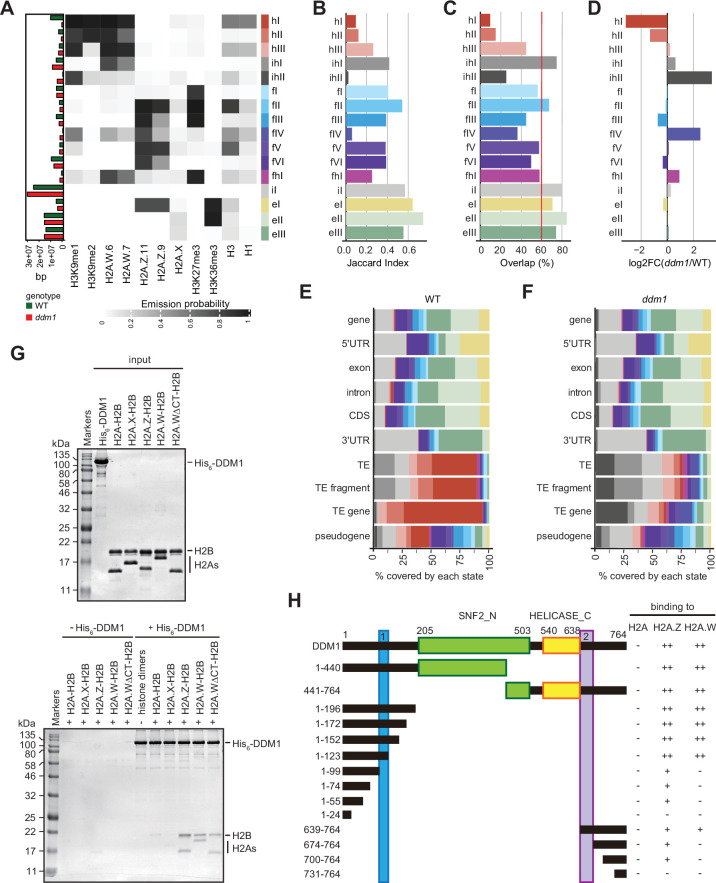
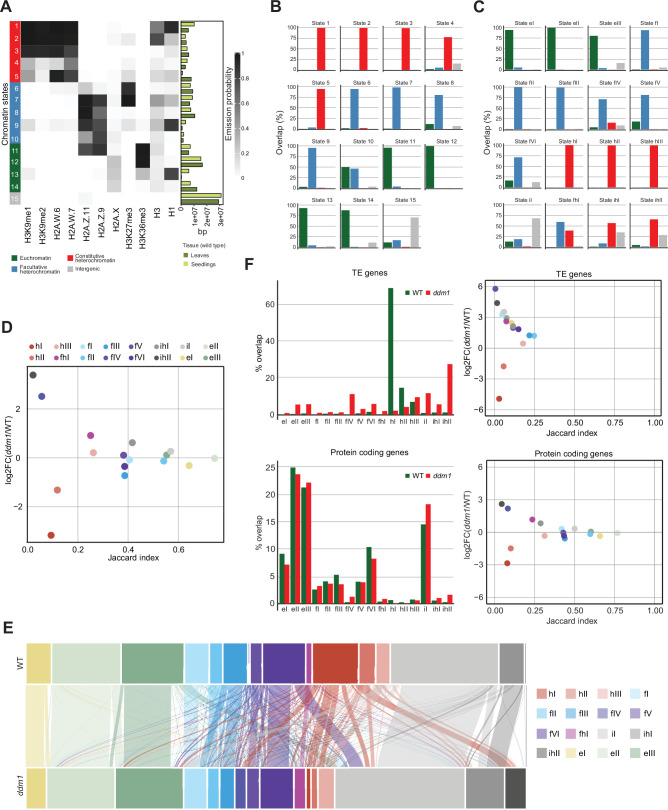
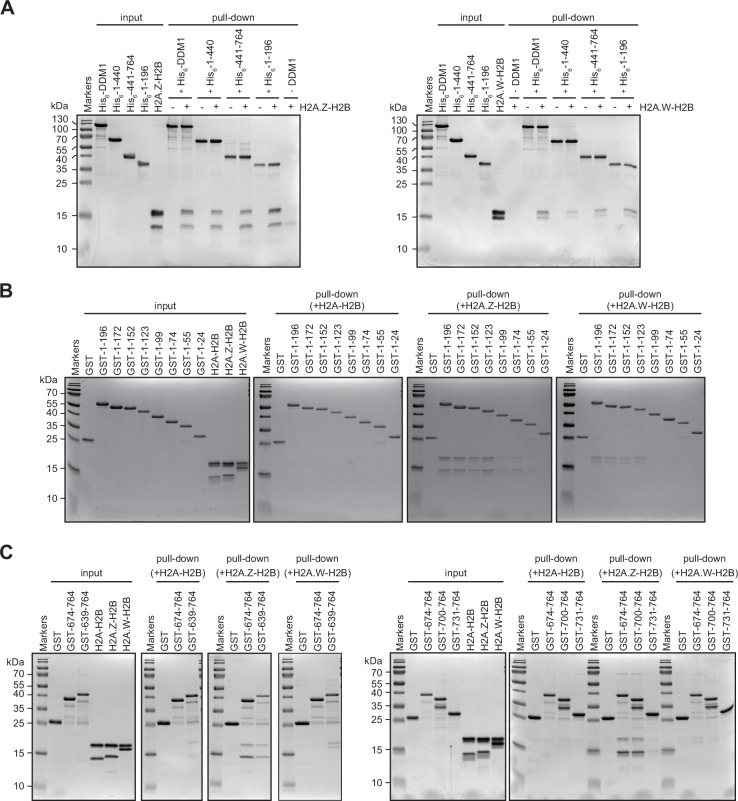
Figure 3. Decreased in DNA Methylation (DDM1) loss of function disrupts chromatin states in Arabidopsis thaliana.
(A) Heatmap showing the emission probability for each mark/variant across the 16 chromatin states of the concatenated wild-type and ddm1 mutant model. The bar plot on the left represents the proportion of the genome covered by each state in wild-type (green) and in ddm1 (red). (B) Bar plot showing the Jaccard indices between the state assignments in wild-type and ddm1 mutant. (C) Bar plot showing the state assignment overlap between the wild-type and ddm1 for each chromatin state. The red vertical line represents the genome-wide overlap (62.2%). (D) Bar plot showing the log2 fold changes of the proportion of genome covered by each state across the ddm1 genome compared to the wild-type. (E) Stacked bar plot showing the overlap between annotated genomic features and chromatin states from the concatenated model in wild-type. (F) Stacked bar plot showing the overlap between annotated genomic features and chromatin states from the concatenated model in ddm1 mutant. (G) DDM1 interaction with H2A.W and H2A.Z. Coomassie-stained 15% SDS-PAGE gel showing input protein samples (top panel) used for in vitro pull-down (bottom panel) with His6-tagged DDM1 and histone dimers. The lane ΔCTH2A.W shows that the deletion of the C-terminal tail of H2A.W does not influence binding to DDM1. (H) Summary of the pull-down assays to identify regions in DDM1 binding to H2A.W and H2A.Z. Blue and purple boxes indicate the H2A.W binding regions in DDM1 identified by previous work (Osakabe et al., 2021). Original pictures of the gels are provided in Figure 3—source data 1.