Figure 2.
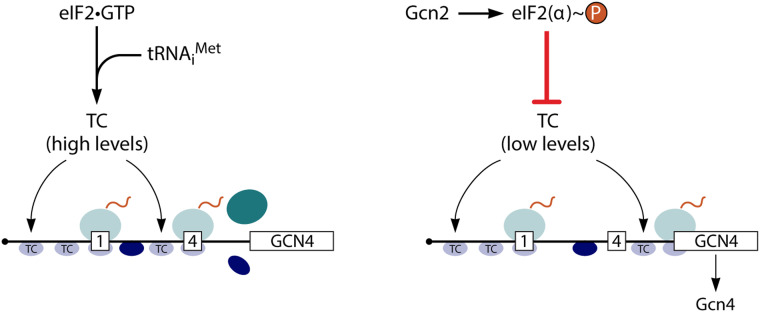
Schematic model of GCN4 translational control, simplified to show only uORF1 and uORF4, which are sufficient for nearly wild-type regulation. Following translation of uORF1 (boxed 1), posttermination 40S subunits remain attached to the GCN4 mRNA and resume scanning. (Left) Under nonstarvation conditions, they quickly rebind TC and reinitiate at uORF4 (boxed 4), and the 80S ribosome dissociates after terminating at uORF4. (Right) Under amino acid starvation conditions, the concentration of TC is reduced by eIF2α phosphorylation, such that many 40S ribosomes fail to rebind TC until after scanning past uORF4 and can thereby reinitiate at the GCN4 ORF instead. (Reproduced from Hinnebusch 2011 with permission from American Society for Microbiology).