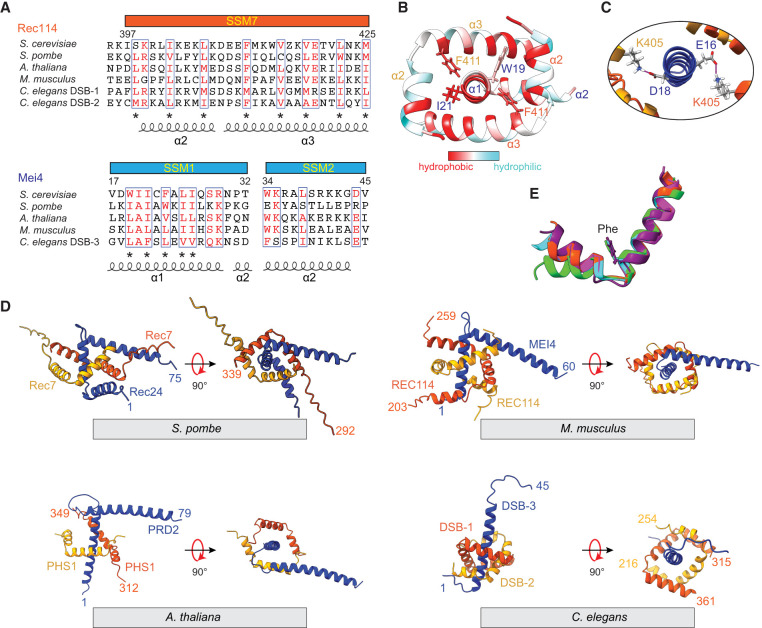
Figure 3.
Structure and conservation of Rec114–Mei4 interactions. (A) Structure-informed alignment of Rec114 and Mei4 orthologs. Secondary structure elements and SSMs are indicated. Conserved residues are highlighted in red, and conserved hydrophobic residues are labeled by asterisks. (B) Hydrophobic interactions at the Rec114C–Mei4N interface. Hydrophobic residues are highlighted in red. (C) Predicted contacts between K405 from each Rec114C chain and either E16 or D18 from Mei4N. (D) AlphaFold2 structural models of equivalent domains for Rec114 and Mei4 orthologs from S. pombe, M. musculus, A. thaliana, and C. elegans. (E) Structural alignment of SSM7 from Rec114 orthologs. The highly conserved phenylalanine is shown (F411 in S. cerevisiae). (Orange-red) S. cerevisiae, (cyan) S. pombe Rec7, (purple) M. musculus REC114, (green) A. thaliana PHS1/AtREC114, (magenta) C. elegans DSB-2.