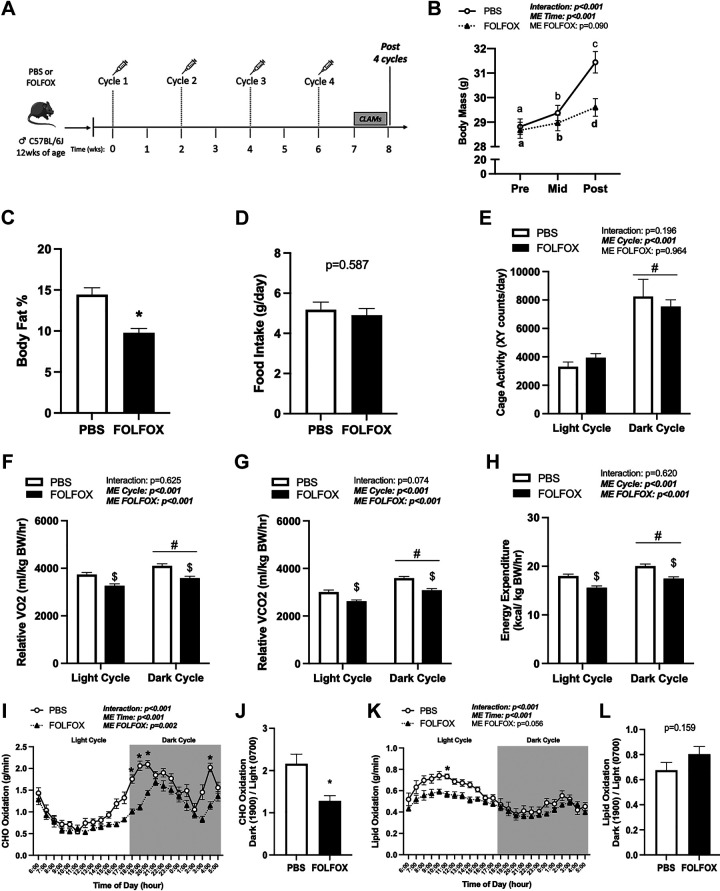
Figure 1.
Four cycles FOLFOX chemotherapy induces deficits in systemic oxygen consumption (V̇o2), energy expenditure, and carbohydrate (CHO) oxidation independent of cage activity. A: study design. Male C57BL/6J mice were administered four cycles of either PBS or FOLFOX (5-FU, oxaliplatin, leucovorin) over 8 wk. Mice were individually housed in CLAMS metabolic cages for 5 days before tissue collection. B: body mass at Pre (0 wk), Mid (4 wk), and Post (8 wk) (PBS: n = 27, FOLFOX: n = 33) and body fat percentage in PBS and FOLFOX mice (C). D: food intake of individually housed mice during CLAMS measurements. Cage activity (E) and relative (normalized to kg body weight) oxygen consumption (V̇o2; F), carbon dioxide production (V̇co2; G), and energy expenditure expressed as the average of the light cycle (H) (0600 to 1700) and dark cycle (1800 to 0500). CHO oxidation (I) and CHO oxidation metabolic flexibility (J). Lipid oxidation (K) and lipid oxidation metabolic flexibility (L). PBS: n = 8, FOLFOX: n = 8. Data are presented as means ± SE. Data are analyzed using two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with post hoc analysis when appropriate (B, E–H, I, K) or unpaired t test (C, D, J, L). Statistical significance was set to P < 0.05. Bold and italic text denotes significance. a,b,cSignificant difference between groups; *different from PBS; #main effect of time/cycle; $main effect of FOLFOX. CHO, carbohydrate; CLAMS, Comprehensive Laboratory Animal Monitoring System; FOLFOX, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin; g, grams; hr, hour; kg, kilograms; kcal, kilocalorie; mL, milliliters; ME, main effect; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.