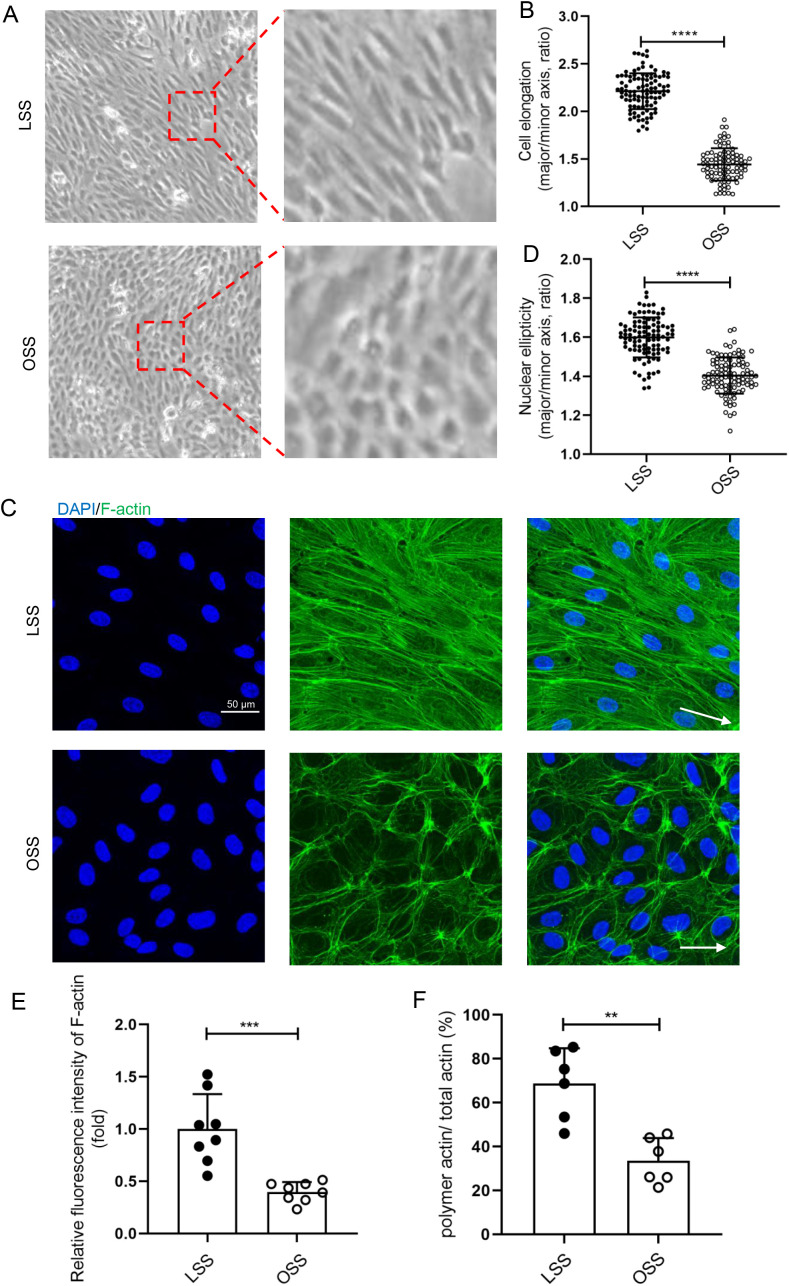
FIG. 3.
OSS inhibited the polymerization of F-actin in vitro. (a) and (c) HUVECs were loaded with LSS (12 dyn/cm2) and OSS (5 dyn/cm2) for 48 h. (a) Representative photomicrographs of HUVECs morphology after mechanical loading. White arrows pointed in the direction of loading fluid. (b) Statistical analysis of the cell elongation (ratio of long axis/short axis of cells) (n > 80). (c) Immunofluorescence staining for F-actin (green) and nuclei (blue) in HUVECs. White arrows pointed in the direction of loading fluid (scale bar = 50 μm). (d) Statistical analysis of nuclear ellipticity (ratio of major axis/minor axis of nucleus) as shown in (c) (n = 100). (e) Statistical analysis of the relative fluorescence intensity of F-actin as shown in (c) (n = 8). (f) Statistical analysis of the polymeric actin ratio (ratio of polymer actin/total actin) as shown in (c) (n = 6). All data were presented as mean ± SD. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, and **** P < 0.0001.