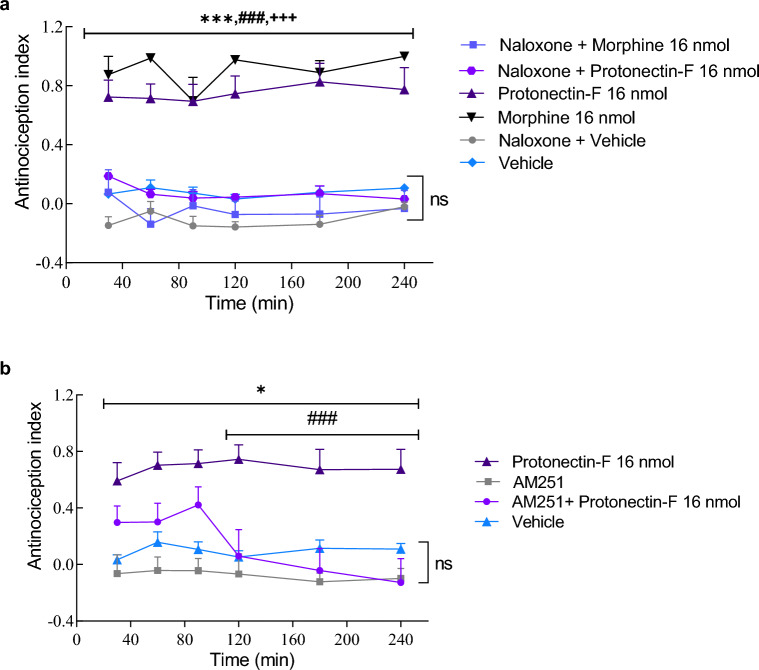
Figure 6.
(A) Antinociception index obtained from the hot plate assay exploring the pharmacological antagonism of naloxone. The antinociceptive effect of protonectin-F (16 nmol) and morphine (16 nmol) was evaluated after administration of naloxone, as well as protonectin-F or morphine alone. Control groups were treated with vehicle alone or with naloxone and vehicle. Data were analyzed by Two-Way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. (***) indicates statistical difference when compared to vehicle control p < 0.001. (###) indicates difference when compared the group treated with naloxone and morphine 16 nmol with p < 0.001. (+ + +) indicates difference when compared to the control group treated with naloxone and protonectin- F with p < 0.001. (B) Antinociception index obtained from the hot plate assay exploring the pharmacological antagonism of AM251. The antinociceptive effect of protonectin-F was evaluated after administration of AM251, as well as protonectin-F alone. Control groups were treated with vehicle or with AM251. Data were analyzed by Two-Way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. (***) indicates statistical difference when compared to vehicle control with p < 0.001. (###) indicates difference when compared the group treated with AM251 and protonectin-F with p < 0.001.