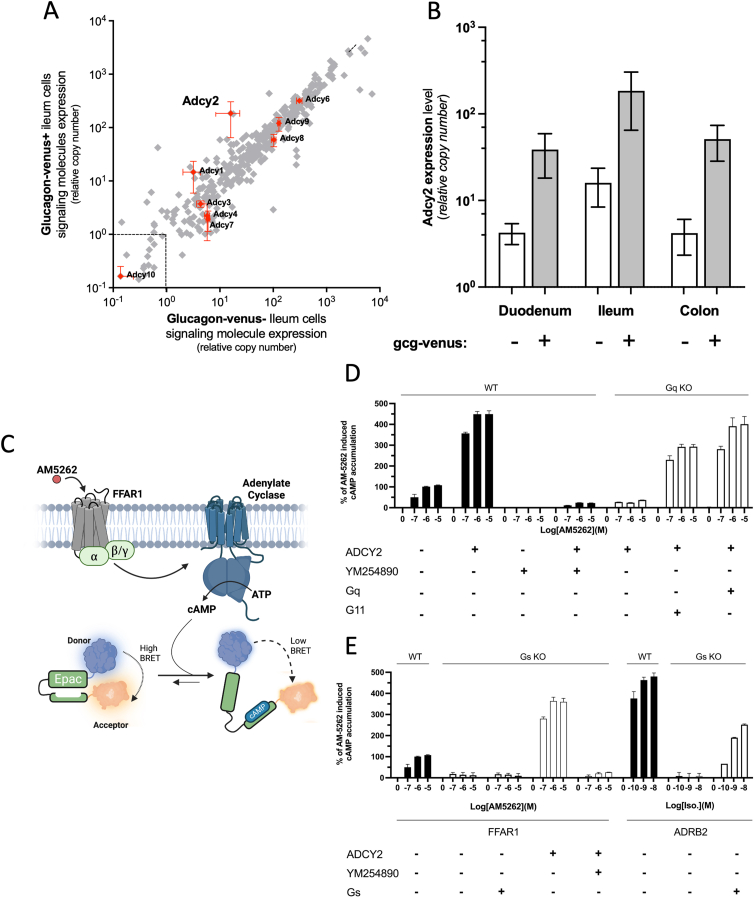
Figure 3.
Identification of ADCY2 as potential mediator of the FFAR1-induced Gq-dependent cAMP accumulation. Panel A– Expression of the ten adenylate cyclases highlighted in orange symbols in FACS purified GLU-Venus positive enteroendocrine GLP-1 cells (y-axis) versus expression in neighboring GLU-Venus negative mucosal cells (x-axis) as determined using a customized qPCR array of GPCR signal transduction genes (grey symbols) in cells isolated from the ileum of proglucagon GLU-Venus reporter mice. Dotted lines indicate detection limit corresponding to CT 35. Panel B – Expression of Adcy2 in FACS-purified GLU-Venus positive cells (grey columns) and negative mucosal cells (open columns) from the duodenum, ileum, and colon of the GLU-Venus reporter mice. Data are from 3 individual experiments, shown with mean ± SEM. Full scattergrams for duodenum and colon are shown in Figure S4. Panel C - Schematic overview of the BRET-based CAMYEL assay used for measuring cAMP accumulation within HEK293 cells (Panels D and E). Panels D and E - FFAR1-induced cAMP accumulation in response to AM5262 10−7 to 10−5 M as % of Emax observed in WT cells without ADCY2 co-transfection in WT HEK293 cells (black columns) and Gαq deficient HEK293 cells (Panel D) and in WT (black columns) and Gαs deficient HEK293 cells (Panel E) (white columns) +/− co-transfection with ADCY2 and +/− Gq inhibitor (YM254890), and +/− reintroduction of Gα proteins as indicated below the panels. To the right in Panel E are as control shown cAMP accumulations in response to isoproterenol in WT and Gs-deficient HEK293 cells transfected with the β2AR without and with reintroduction of Gs as indicated. Bars and error represent the mean ± SEM for 3 three independent experiments performed in triplicate.