Extended Data Figure 6: B7-H3 CAR design with avidity, synapse, and calcium flux analyses.
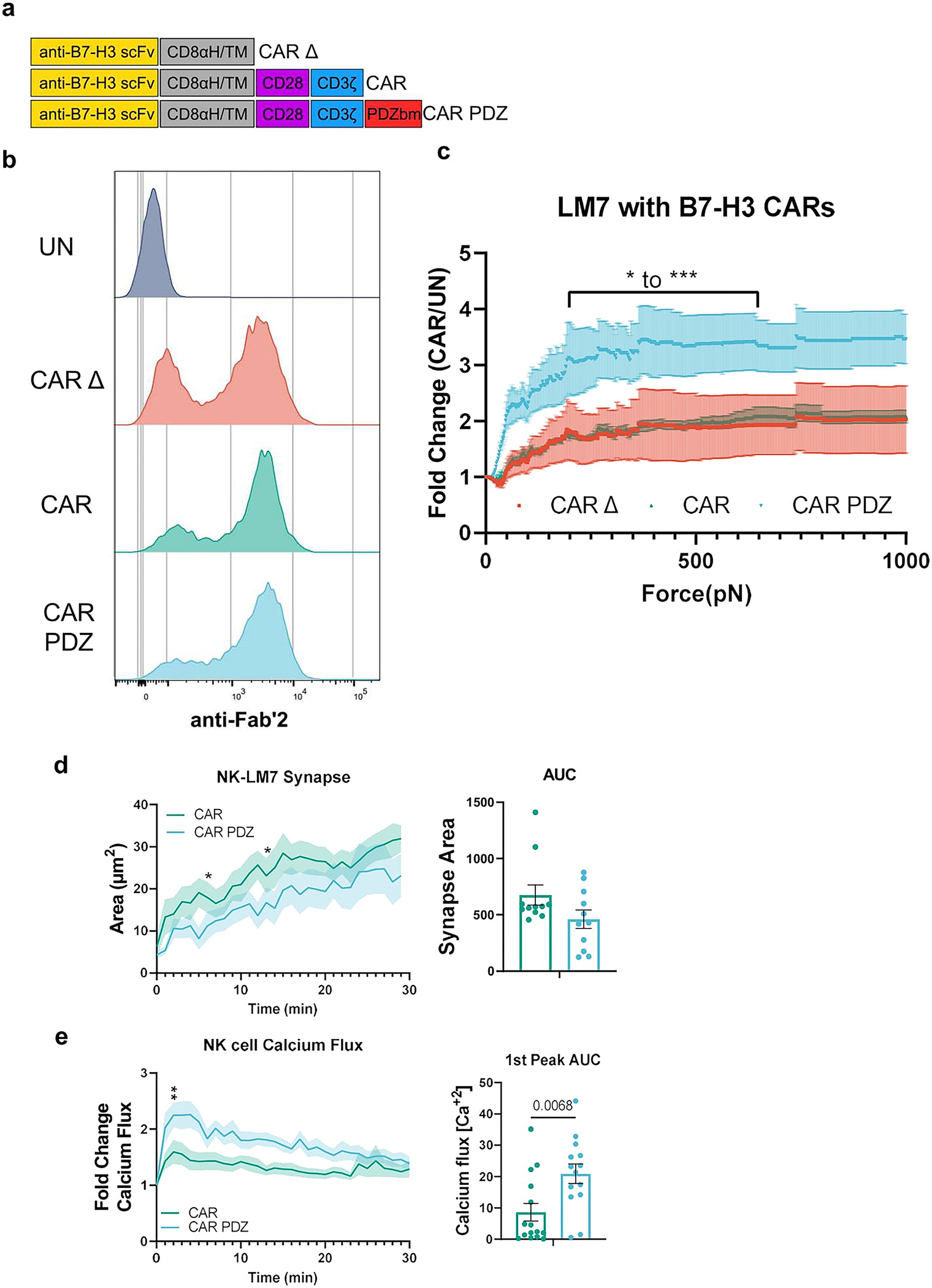
(a) Chimeric antigen receptor design schemes. Antigen recognition domain (anti-B7-H3 scFv): goldenrod, hinge and transmembrane domains (CD8αH/TM): grey, CD28 co-stimulatory domain: purple, CD3ζ activation domain: blue, PDZbm scaffolding anchor domain: red.
(b) Example flow cytometry plot detailing B7-H3 CAR expression.
(c) Normalized fold change of CAR NK cell binding compared to untransduced NK cells. Bracketed line indicates the scale of statistical difference at CAR.PDZ vs. CAR Δ and CAR from 194 to 646pN for both comparisons except for 205–215pN. Two-Way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance with Two-stage linear step-up procedure of Benjamini, Krieger and Yekutieli to correct for FDR; q<0.05 *, <0.001 ***, n=3 donors, mean±SEM shown.
(d) Immune synapse area quantification of B7-H3 CAR and CAR.PDZ NK cells (n=11 and 11 cells) Two-Way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance with Uncorrected Fisher’s LSD test p<0.05 * at minute 5 and 12 with area under the curve analysis.
(e) Calcium flux quantification of B7-H3 CAR and CAR.PDZ NK cells (n=15 and 14 cells) with Two-Way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance with Uncorrected Fisher’s LSD test p<0.05 * starting at minute 2; 1st peak AUC analysis with unpaired Student’s t-Test, mean±SEM shown of one donor.
