Fig. 2.
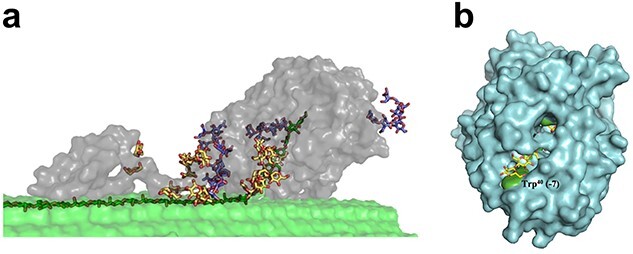
Structure and cellulose binding of a GH family 7 cellobiohydrolase. (a) Structure of the CBH TrCel7A from T. reesei, comprised of a catalytic domain (CD) (right grey part), a CBM (left grey part), and a connecting linker domain, bound to cellulose (Greene et al., 2015). The enzyme acts on a single cellulose chain that needs to be extracted from its crystalline context (dark green carbons) and guided into the catalytic tunnel. The structures shown with yellow and blue carbons are O-glycans on the linker and CBM, and N-glycans on the catalytic domain, respectively. This picture was taken from Taylor et al. (2018). (b) Structure of the catalytic domain of TrCel7A bound to cellononaose (PDB code 4C4C; the sugar molecule has yellow carbons) (Knott et al., 2014). The picture provides a view on the substrate-binding tunnel that contains four conserved tryptophan residues (Trp38, Trp40, Trp367 and Trp376; green) that are stacking with the cellulose substrate, as shown in Fig. 3. Trp40, at what has been called the tunnel ‘entrance’, corresponding to the −7 subsite, is labeled.
