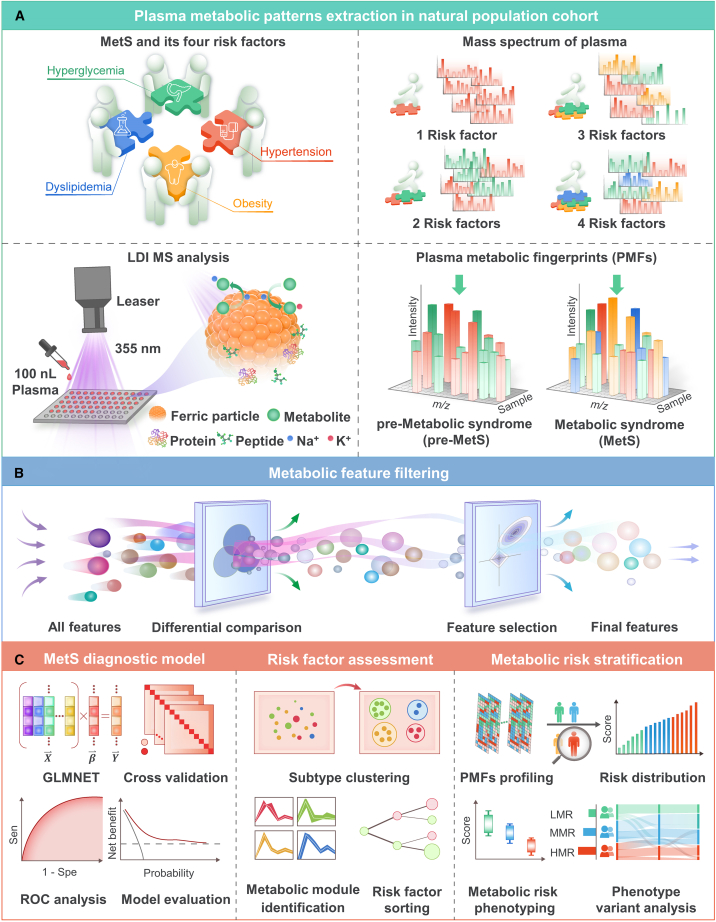
Figure 1.
Overall schematics for evaluating MetS among the general aging population based on the combination of PMFs and ML
(A) Schematic workflow for the extraction of PMFs using ferric particle-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (LDI-MS). One hundred nanoliters of native plasma was used for direct analysis without pretreatment procedures. Only Na+- and K+-adducted metabolites can be selectively detected with the coexistence of high concentrations of peptides and proteins.
(B) Feature filtering for hub PMFs was carried out according to difference comparisons among the healthy control (HC), pre-MetS, and MetS groups.
(C) PMF-based diagnostic models were constructed for HC vs. pre-MetS, pre-MetS vs. MetS, and HC vs. MetS. Traditional risk factors were assessed by unsupervised clustering of various subtypes of MetS. Finally, PMF-based metabolic risk stratification was computed to define three metabolic risk patterns: low metabolic risk (LMR), moderate metabolic risk (MMR), and high metabolic risk (HMR).