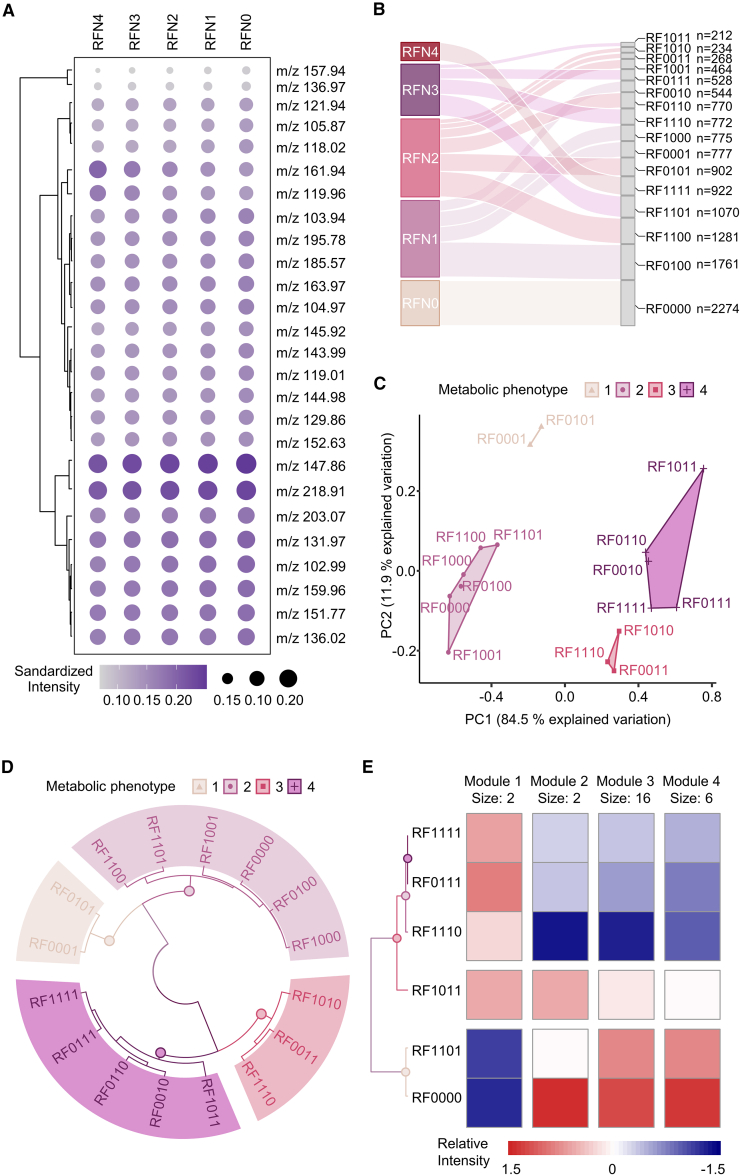
Figure 4.
PMF-based unsupervised ML revealed the heterogeneity of MetS
(A) The standardized intensity of all hub PMFs among five subgroups (RFN0–RFN4) according to the number of risk factors.
(B) The distribution of five subgroups (RFN0–RFN4) and 16 subclusters (RF0000–RF1111) classified according to traditional risk factors in the general population.
(C) K-means clustering analysis scatter diagram regrouping 16 subclusters into four metabolic phenotypes (MPs) based on the results of PCA. Each point represents a subcluster condition containing (or not) the risk factor according to Table 2. MPs are indicated by colored shading.
(D) Circular hierarchical cluster analysis dendrogram grouping 16 subclusters into the same four MPs based on phenotypic similarity. Colors of subcluster names based on the MPs.
(E) Relative risk assessment among the five MetS subgroups (RF0111, RF1011, RF1101, RF1110, RF1111) and HC group through K-means clustering analysis based on the relative intensity of all 26 hub PMFs. These PMFs were divided into four metabolic feature modules (modules 1–4).