Figure 4.
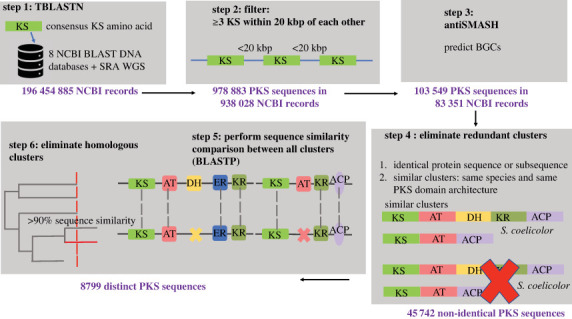
Overview of workflow used to curate the catalogue of distinct, non-redundant assembly line PKSs. (1) TBLASTN analysis of a consensus KS amino acid sequence against 8 NCBI BLAST nucleotide databases as well as SRA whole genomic shotgun sequencing database. The consensus KS sequence is available on our Github page. (2) Identify sequences with at least 3 KS domains within 20 kbp of each other. (3) Run antiSMASH algorithm on sequences remaining after filtering in step 2 to annotate PKS domains and boundaries. (4) Eliminate identical PKSs based on amino acid sequence analysis, domain architecture and species. (5) A customized BLASTP-based algorithm to estimate sequence similarity of each assembly line PKS to every other non-redundant PKS. (6) Eliminate homologous PKSs based on sequence similarity score from step 5. If any two PKSs had greater than 90% similarity score, only one distinct PKS was retained for the catalogue.
