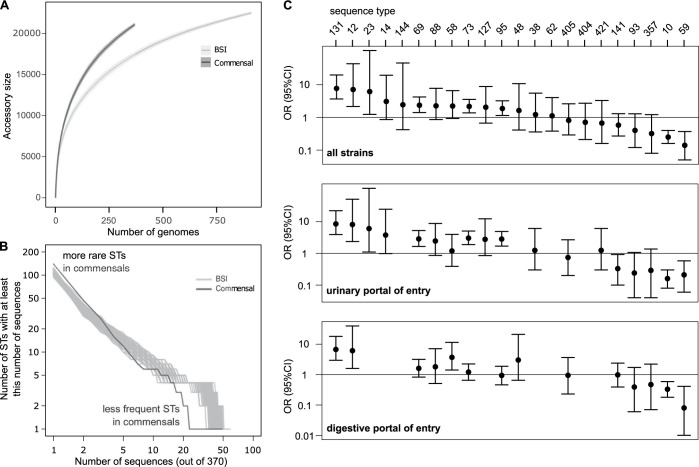
Fig 2. Comparison of the global phylogenomic characteristics of the commensal and BSI collections.
(A) Pangenome sizes as a function of the number of genomes analyzed for the BSI (912 strains) and commensal (370 strains) collections, showing the greater pangenome size of the commensal collection. (B) Cumulative distribution of strain sequences within ST in commensal and BSI collections. To be able to compare the BSI collection with the smaller commensal collection (N = 370), we extracted 200 random sub-samples of 370 sequences from the BSI collection (grey curves). (C) Comparison of the distribution of the sequence types (STs) of the E. coli commensal and BSI collections isolates (see S2 Table). We show the odds ratio (OR with 95% CI) for the risk of infection associated with colonization by each ST (logistic model of infection status as a function of the ST). We selected the STs present in at least 5 strains in at least one of the two collections. STs are ordered by decreasing associated odds ratio for all strains.