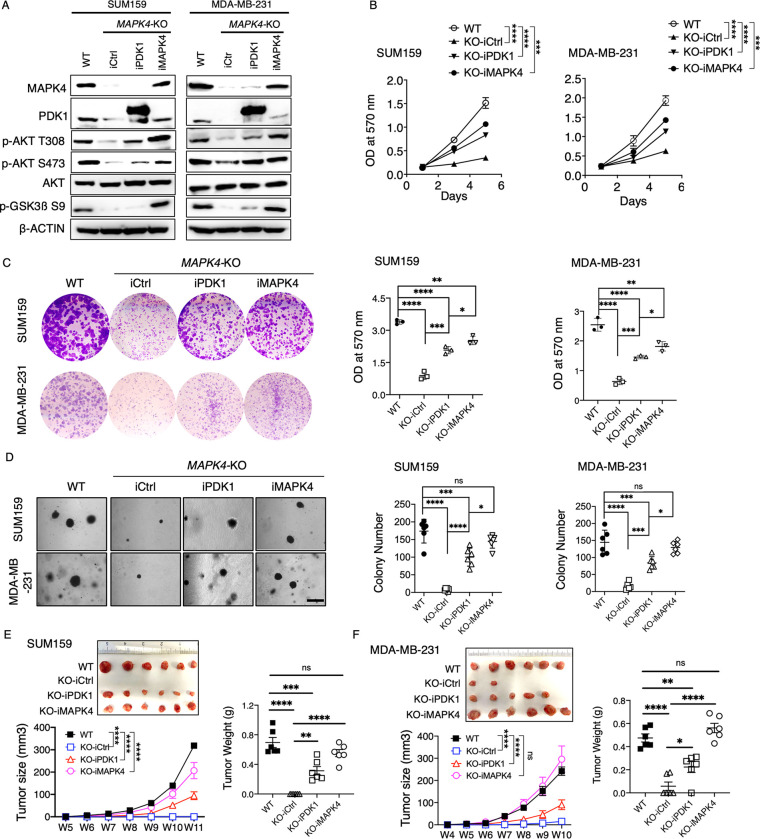
Fig 3. Overexpression of PDK1 partly rescues MAPK4-KO tumor cell growth.
(A) Western blots, (B) proliferation assays, (C) plate colony formation assays, and (D) soft-agar assays on WT or engineered MAPK4-KO SUM159 and MDA-MB-231 cells with 0.5 μg/ml Dox-induced expression of PDK1 (iPDK1), MAPK4 (iMAPK4), or control (iCtrl). Scale bar: 500 μm. (E, F) 1 × 106 WT or the engineered MAPK4-KO SUM159 and MDA-MB-231 cells with Dox-inducible expression of PDK1 (iPDK1), MAPK4 (iMAPK4), or control (iCtrl) in 1:2 Matrigel were injected into the mammary fat pad of SCID mice. All mice also received 0.5 mg/ml Dox in drinking water. Tumors were measured and harvested as indicated. Shown are the tumors’ images at collection, growth curve (means ± SEM), and weights. Quantification data as means ± SD other than otherwise indicated. P values by one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001. ns, not significant. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. The numerical values underlying the figures can be found in S1 Data. MAPK4, mitogen-activated protein kinase 4; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; WT, wild type.