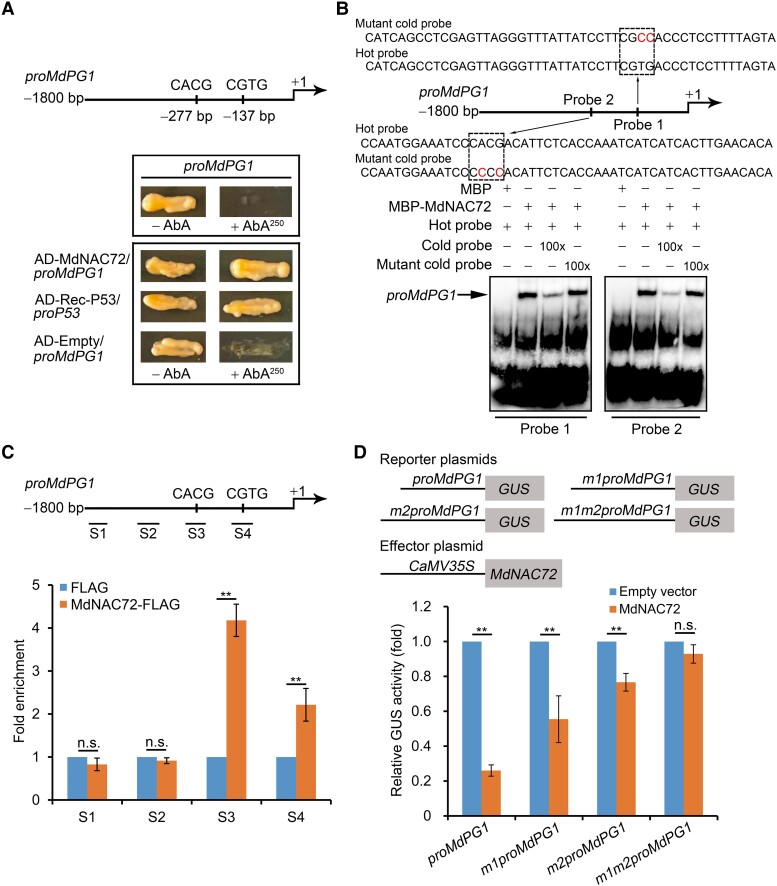
Figure 4.
MdNAC72 represses MdPG1 transcription by binding to its promoter. A) Y1H assay showing that MdNAC72 directly binds to the MdPG1 promoter. The basal concentration of AbA (aureobasidin A) used was 250 ng mL–1. The empty vector and the MdPG1 promoter were used as negative controls. The Rec-P53+P53-promoter was used as a positive control. B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) to assess the binding of MdNAC72 to the CACG or CGTG binding sites in the MdPG1 promoter. The hot probes (probe 1 and probe 2, Supplemental Data Set 4) were biotin-labeled fragments of the MdPG1 promoter containing the NAC binding site. The cold probes were unlabeled and used as competitive probes (100×). The mutant cold probe consisted of an unlabeled hot probe with 2 nucleotides mutated. Recombinant MdNAC72-MBP was purified from E. coli and used for DNA-binding assays. C) ChIP-qPCR assay showing that MdNAC72 binds to the MdPG1 promoter in vivo. The various crosslinked chromatin samples were extracted from MdNAC72-FLAG apple fruit calli and immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody. The eluted DNA was used to amplify the sequences neighboring the NAC binding site using qPCR. Four different regions (S1–S4) were investigated. Fruit calli injected with the empty vector (35S:FLAG) were used as a negative control. The ChIP-qPCR assay was performed 3 times, and the enriched DNA fragments in each ChIP were considered 1 biological replicate for qPCR. Values are means ± Se. Statistical significance was determined using Student's t-test (**P < 0.01). n.s., no significant difference. D) β-glucuronidase activity assay showing that MdNAC72 represses MdPG1 promoter activity. The 35S:MdNAC72 effector vector together with the proMdPG1:GUS promoter, or a mutated promoter (m1proMdPG1, m2proMdPG1, and m1m2proMdPG1), were infiltrated into N. benthamiana leaves to analyze GUS activity. The 35S:LUC was included as an internal control for normalization of transformation efficiency. Three independent infiltration experiments were performed; values are means ± Se. Statistical significance was determined using Student's t-test (**P < 0.01). n.s., no significant difference.