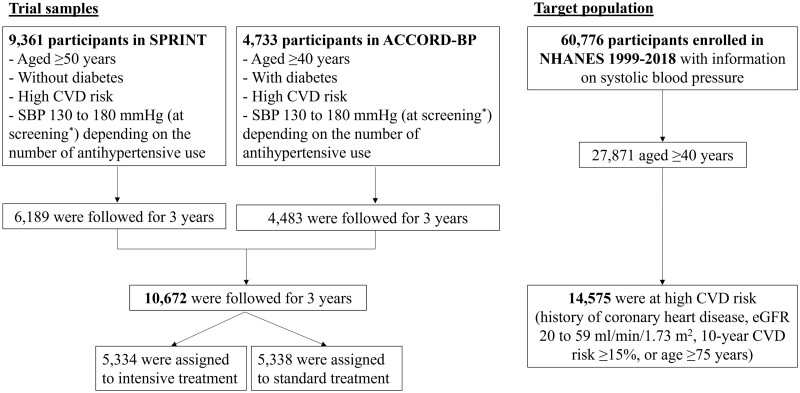
Figure 1.
The flow of the study sample. SPRINT, Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial; ACCORD-BP, Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Blood Pressure; NHANES, National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey; SBP, systolic blood pressure; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; CVD, cardiovascular disease. The SPRINT trial included 9361 adults without diabetes in the USA. The key inclusion criteria included: age ≥50 years, SBP 130–180 mm Hg at screening and high CVD risk (i.e. the presence of clinical or subclinical CVD, chronic kidney disease, 10-year Framingham risk score ≥15% or age ≥75 years). The ACCORD-BP included 4733 adults with diabetes and glycated haemoglobin levels ≥7.5%. The key inclusion criteria included: age ≥40 years with clinical CVD or age ≥55 years at high CVD risk (atherosclerosis, albuminuria, left ventricular hypertrophy, or ≥2 CVD risk factors (dyslipidaemia, hypertension, smoking or obesity)), SBP 130–180 mm Hg on ≤3 antihypertensive use at screening and urinary protein excretion <1.0 g/day. *Although the eligibility criteria for both trials included SBP 130–180 mm Hg at screening, one-third of participants showed SBP ≤132 mmHg at baseline in both SPRINT and ACCORD-BP.10,11,14 More details are described in Supplementary Figure S1 (available as Supplementary data at IJE online)