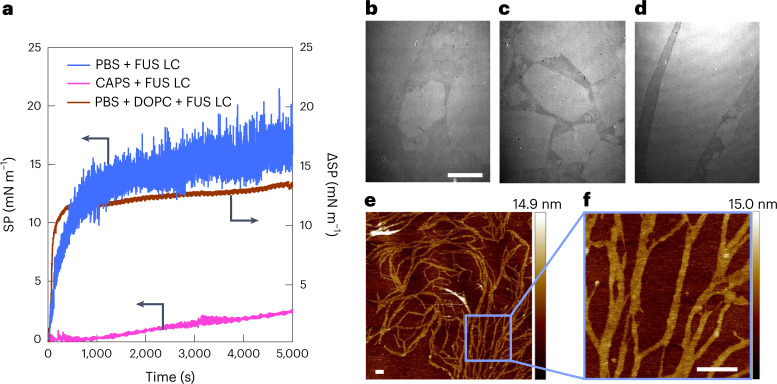
Fig. 1. Mechanical and structural properties of FUS LC at an air/buffer solution interface.
a, SP change versus time for samples of FUS LC in PBS and CAPS buffers (blue and magenta, resp., left axis), and a DOPC phospholipid monolayer spread at 20 mN m−1 at the air/PBS interface (brown, right axis), after the addition of FUS LC to a final bulk concentration of 1.5 μM (in PBS and CAPS) or 3 μM (in PBS with DOPC monolayer) at t = 0. The strongly fluctuating SP for PBS (absent for CAPS and DOPC) is attributed to solid domains colliding with the needle recording the surface tension. b–d, BAM images recorded 2 h (b), 4 h (c) and 5 h (d) after addition of 1.5 μM FUS LC in PBS (at t = 0), showing the appearance of plate-like domains on the surface. Scale bar, 100 μm (b–d). e,f, AFM image of the FUS LC protein film formed at the air/PBS buffer interface and deposited on a silicon wafer (e) and zoomed-in image (f). Scale bars, 250 nm (e,f). Vertical colour bars represent height in nm.