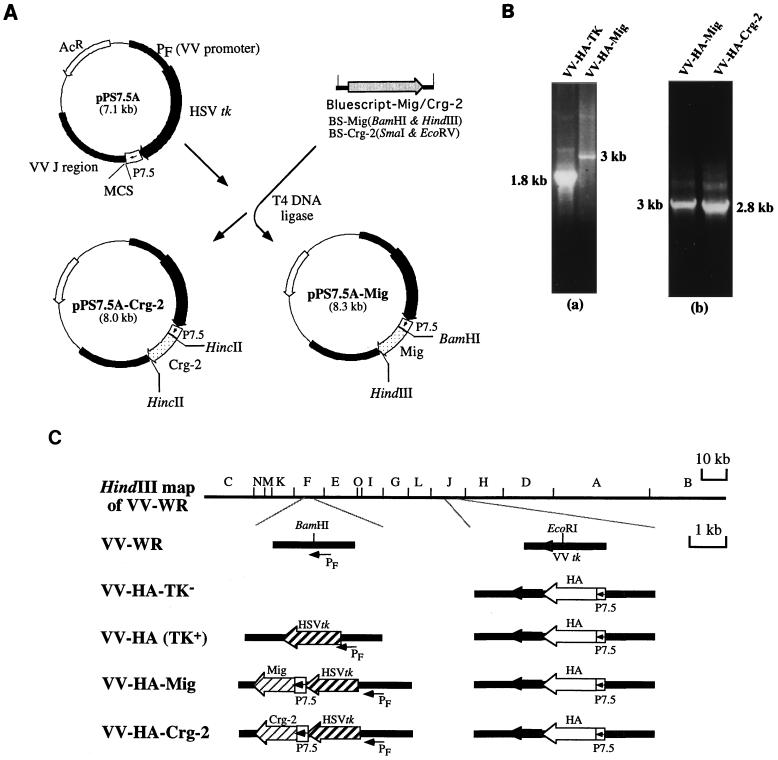
FIG. 1.
(A) Construction of insertion plasmids pPS 7.5-Mig and pPS 7.5-Crg-2. The MuMig or Crg-2 fragment was subcloned into vector pPS 7.5A. The gene fragment was inserted in front of a P7.5 promoter in pPS7.5A. (B) PCR of VV DNA. VV DNA was prepared and was amplified by PCR with primers as described in Materials and Methods. DNA from VV-HA-TK yielded a band of 1.8 kb (panel a) while DNA from VV-HA-Mig and VV-HA–Crg-2 yielded bands of 3 and 2.8 kb respectively (panels a and b). Wild-type virus DNA (VV-PR8-HA6) was also amplified. The presence of a wild-type band was not detected in any of the recombinant viruses constructed. (C) Schematic representation of the genomic arrangements of VVs. The HA gene of influenza virus, under the control of the P7.5 promoter, was inserted into the TK gene of vaccinia virus in the HindIII J fragment, yielding VV-HA-TK−. The disruption of the TK phenotype was compensated for by insertion of an HSV TK gene in the F fragment under the PF promoter. This gave rise to VV-HA-TK+, which was used as the control virus. Marker rescue of VV-HA-TK− with pPS7.5-Mig or pPS7.5–Crg-2 containing HA and Mig or Crg-2 genes produced VV-HA-Mig or VV-HA–Crg-2. PF, VV promoter; P7.5, VV early/late promoter.